This tutorial demonstrates how to enable or disable advanced indexing options in Windows 10 and Windows 11. Included are detailed step-by-step instructions that explain how to configure advanced indexing options in Windows, as well as explanations of what search indexing is, and how optimizing Windows search can improve overall search or system performance.
How to access advanced indexing options in Windows 10 and Windows 11
Access to advanced indexing options is enabled in Windows 10 and Windows 11 by default. These options can be found in the legacy Control Panel:
- Right-click on the Start button and click Run
- In the run dialog, enter control and press OK to open the Windows Control Panel
- Set View by: to Large icons and open Indexing Options from the list of Control Panel items
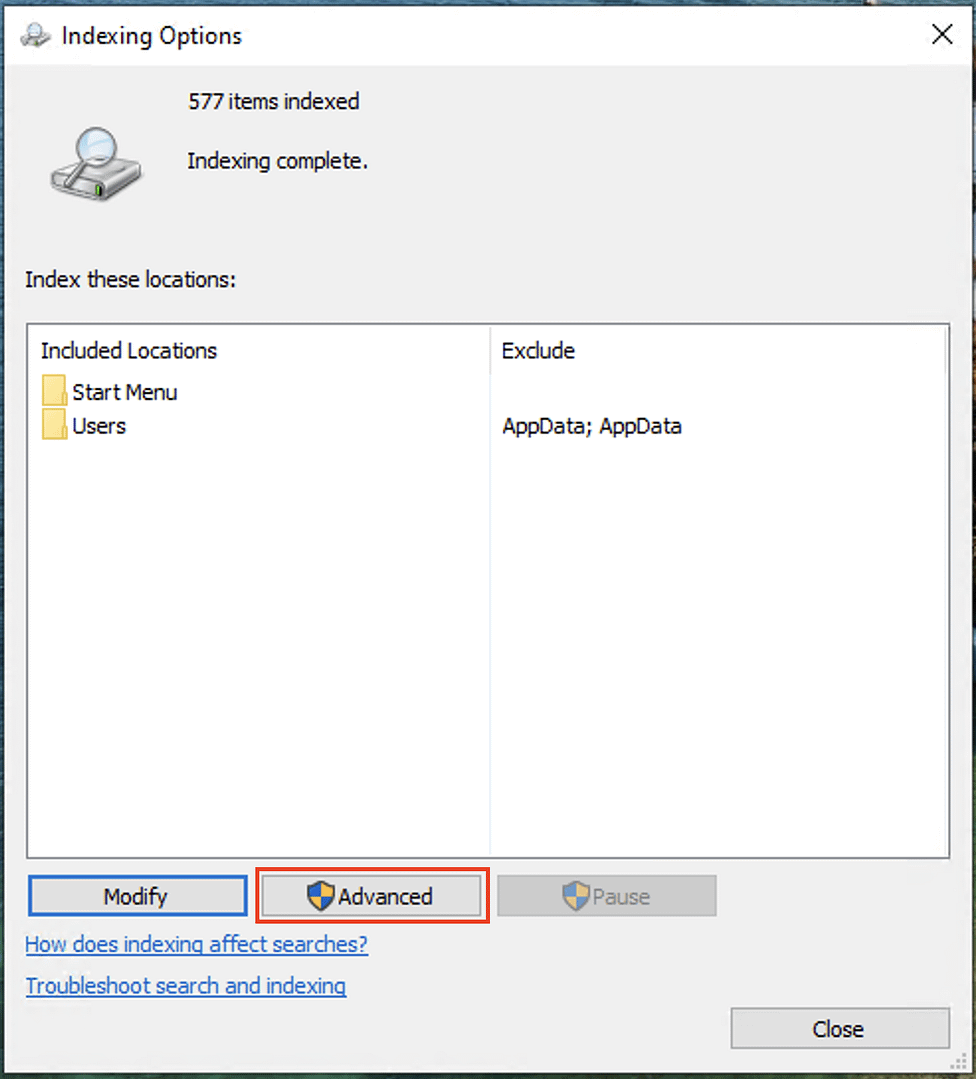
- In the Indexing Options window, click the Advanced button
Note that if advanced search indexing options is disabled, the Advanced button will be greyed out and unavailable.
Enabling advanced indexing options in Windows 10 and Windows 11
You can enable advanced indexing options in Windows using Local Group Policy or via the Windows Registry Editor. Before you make changes to your system, you should back up your important data. If you’re making changes to the registry you can also back up and restore registry data.
Both methods require that you be logged in as an administrator. Note that Local Group Policy is available only in Enterprise, Pro, and Education editions of Windows (and is not available in Windows 10/11 Home).
Enable advanced indexing options with Local Group Policy
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor
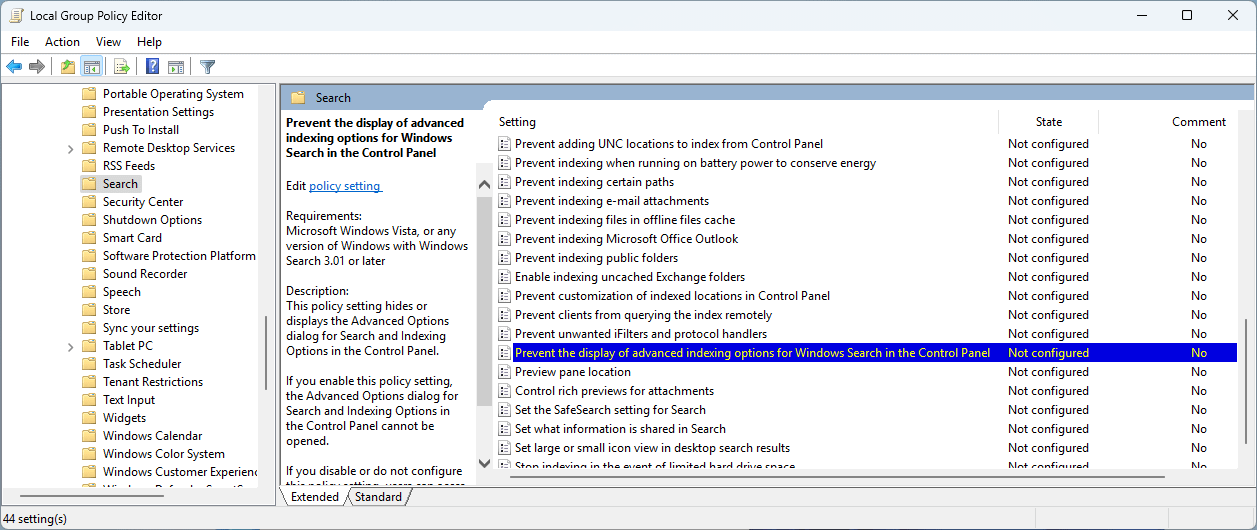
- Go to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Search in the left panel navigation tree
- Locate the Prevent the display of advanced indexing options for Windows Search in the Control Panel setting in the list in the right panel and click on it
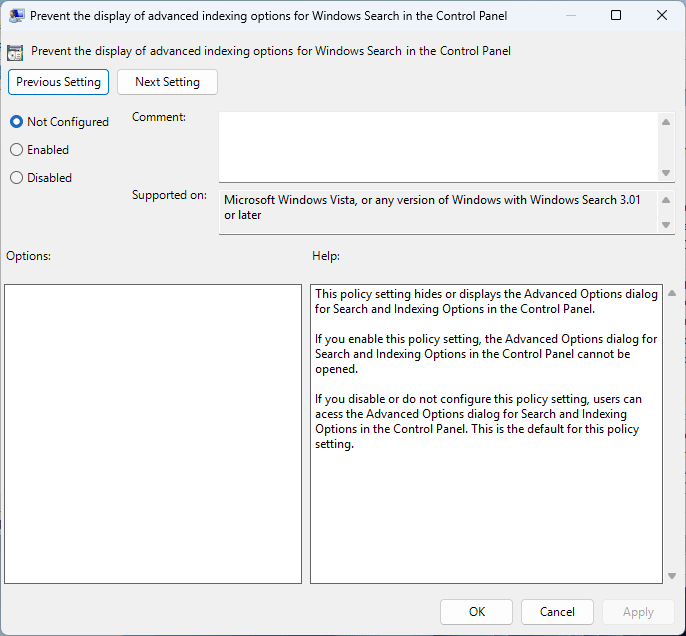
- Select Not configured or Disabled to enabled advanced indexing options
Selecting Not configured enables access to advanced indexing options from the Control Panel, the default behavior.
Enable advanced indexing options with the Registry Editor
- Open the Windows Registry Editor
- Go to the path Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows in the Registry Editor (or copy and paste this path into the navigation bar)
- If a key named Windows Search does not exist at this location, advanced indexing options is enabled by default.
- If the Windows Search key does exist, select it
- Within the Windows Search key, if the value PreventUsingAdvancedIndexingOptions is not present, advanced indexing options is enabled by default
- If it is present, right-click on the key and delete it to enable access to advanced indexing options in the Control Panel
Disabling advanced indexing options in Windows
Disabling advanced indexing options ‘grays out’ the button to access it in the Control Panel, preventing users from configuring them.
Disable advanced indexing options with Local Group Policy
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor
- Go to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Search in the left panel navigation tree
- Locate the Prevent the display of advanced indexing options for Windows Search in the Control Panel setting in the list in the right panel and double-click on it
- Select Enabled disable access to advanced indexing options from the Control Panel
Disable advanced indexing options with the Registry Editor
- Open the Windows Registry Editor
- Navigate to the path Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows in the Registry Editor (or copy and paste this path into the navigation bar)
- If a key named Windows Search does not exist at this location, click Edit > New > Key from the toolbar and create a new key named Windows Search
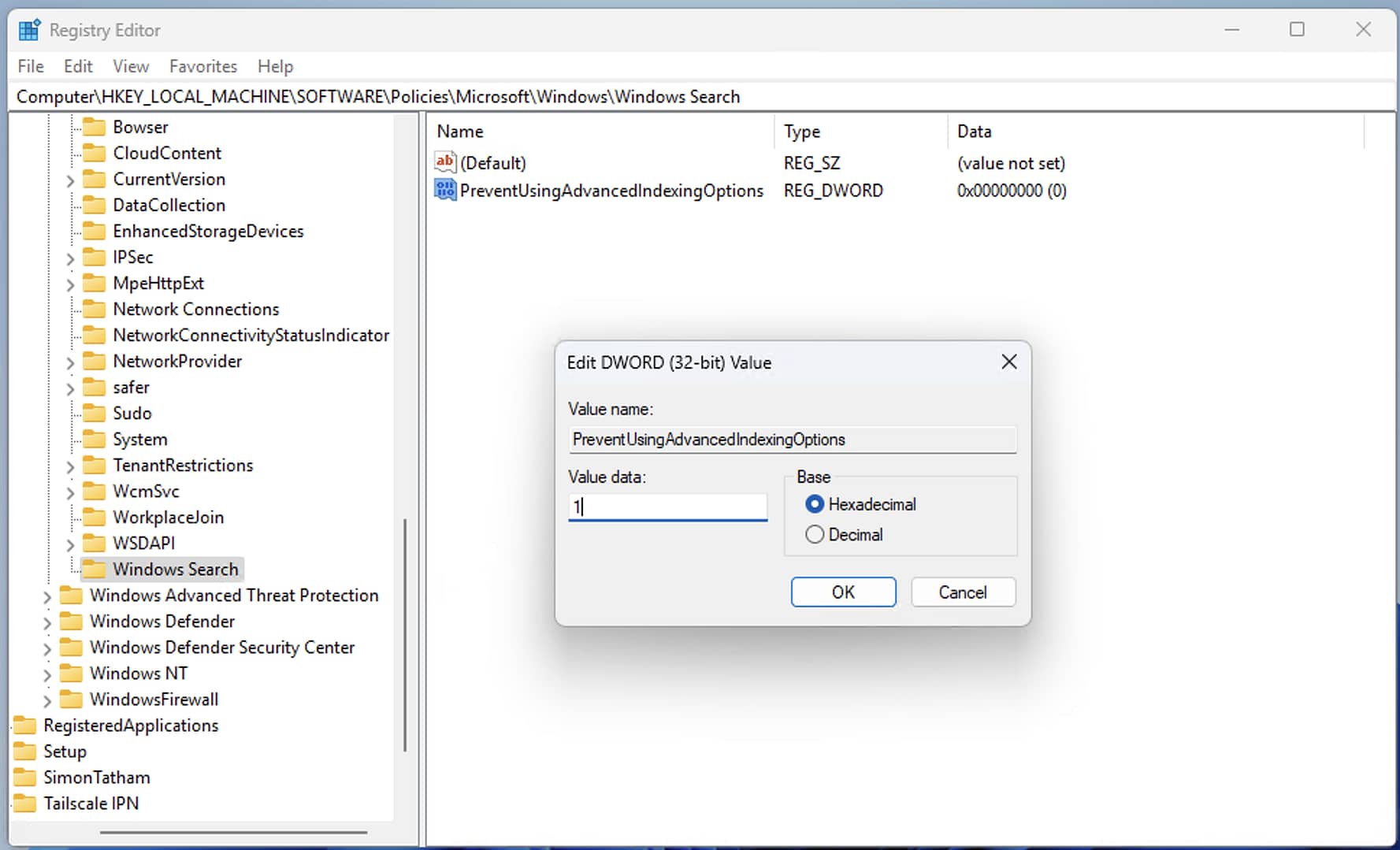
- With the Windows Search key selected, click Edit > New > DWORD (32-bit) Value from the toolbar and name the new DWORD PreventUsingAdvancedIndexingOptions
- Double-click on the PreventUsingAdvancedIndexingOptions DWORD that was just created, and set its value to 1
Configuring advanced search indexing options
Advanced search indexing options allows you to perform several configuration tasks:
- Choose whether encrypted files should be indexed.
- Delete and rebuild the search index to resolve search problems or poor search performance.
- Change the location of the index so that you can manage disk usage.
- Specify the file types that should be indexed, and whether file contents should be indexed.
Windows search indexing and advanced indexing options explained
To make the files on your Windows PC searchable, an index of them is kept. This is a catalog of information about the files, including information such as filenames, creation dates, content, and metadata. This information is stored in a database on your hard disk that is regularly updated as files are created, deleted, and edited. Maintaining an up-to-date search index makes the files it describes faster to search for.
By default, Windows search does not index all the files on your storage devices. This is for both practical and performance reasons: you probably don’t need to be searching the files that make your apps or the Windows operating system function (they would just clog up the search results, making your documents and personal files hard to locate), and omitting irrelevant files makes search more efficient, spending system resources indexing only the files you are going to search for.
Windows search advanced indexing options allows you to configure the behavior of search indexing. This includes specifying which files to index for fast searching, as well as the specific file types to index.
Reasons to configure advanced indexing options
Search is a key function of every operating system, and is vital for many users’ workflows. Search performance and resource usage can be enhanced by omitting files that you know in advance that you will not need to search, or that do not contain searchable information.
For example, on Windows PCs that are primarily used for gaming rather than productivity, search indexing can be limited or disabled so that it does not impact performance without impacting the user as they never need to search a large library of documents.
On a workstation used for business, users may specify that PDF, Word, and Excel documents in specific folders are indexed regularly. Files that include sensitive information covered by customer/user privacy laws can also be omitted from indexing, meaning the data remains only in the files themselves.
Managing search in enterprises
Keeping configurations (including access to advanced indexing options) consistent across fleets of devices to ensure consistent behavior and security policies is vital for smooth enterprise IT operations.
NinjaOne provides a complete endpoint management solution for enterprise and education that lets you deploy configuration changes, monitor for and preemptively resolve issues using automation, and remotely assist users with any issues.