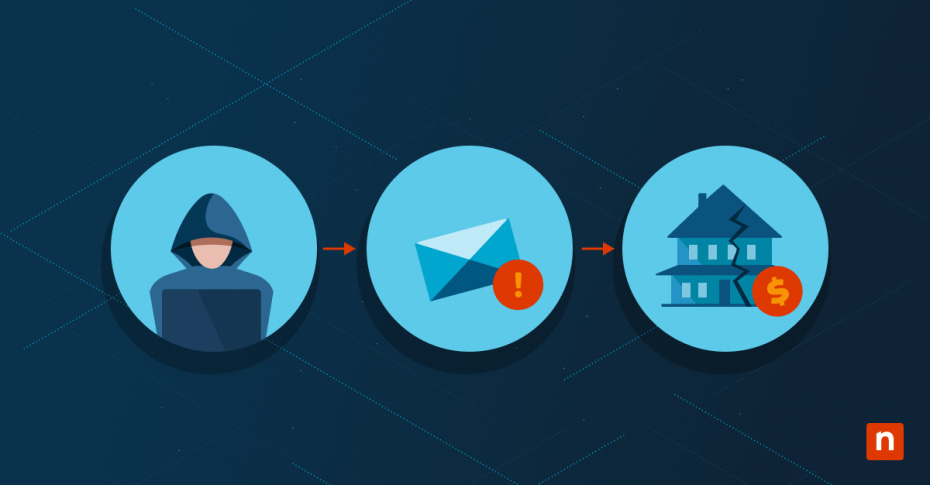
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a type of cyberattack where attackers use email to exploit businesses by deceiving employees into transferring money or sensitive information. These attacks often involve impersonation of company executives or trusted business contacts to trick recipients into performing specific actions. As businesses become more reliant on digital communication, the threat of BEC grows, making it essential for organizations to recognize and mitigate these risks effectively.
This guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of Business Email Compromise (BEC), explaining what it is, how it works, its impact on businesses, and strategies for prevention and mitigation.
How Business Email Compromise works
Common tactics used by attackers
Attackers commonly use several tactics in BEC attacks, including:
- Phishing: Sending fraudulent emails to trick recipients into providing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
- Spoofing: Creating email addresses that resemble those of legitimate contacts to deceive recipients.
- Social engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
Step-by-step breakdown of a typical BEC attack
A typical BEC attack can be broken down into the following steps:
- Reconnaissance: Attackers gather information about the target organization and its key personnel.
- Infiltration: Using phishing or spoofing, attackers gain access to the email system.
- Impersonation: Attackers impersonate executives or trusted contacts to send fraudulent emails.
- Execution: The victim is deceived into transferring money or sharing sensitive information.
- Extraction: Attackers withdraw the stolen funds or use the information for further attacks.
Examples of real-world BEC incidents
Real-world BEC incidents illustrate the severe impact these attacks can have:
- Facebook and Google: Between 2013 and 2015, both companies lost $121 million to a Lithuanian hacker who posed as a vendor using phishing emails and forged documents.
- Government of Puerto Rico: In 2020, $2.6 million was lost after hackers impersonated officials and requested a change in bank account details for remittance payments. The FBI froze the funds before they were fully stolen.
- Toyota Boshoku Corporation: In 2019, this company transferred $37 million to fraudulent accounts following a BEC scam where attackers posed as business partners.
- Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta: The hospital lost $3.6 million after fraudsters impersonated the CFO and requested payments to a new bank account using fake letterheads and spoofed domains.
- Save the Children: In 2018, the charity lost $1 million when attackers compromised an employee’s email account and sent fraudulent invoices.
Types of Business Email Compromise attacks
- CEO fraud: CEO fraud involves attackers impersonating a company executive, typically the CEO, to deceive employees into transferring funds or disclosing sensitive information.
- Account compromise: In an account compromise, attackers gain access to an employee’s email account to send fraudulent messages from within the organization, making the attack more convincing.
- Fake invoice schemes: These involve attackers sending fraudulent invoices to businesses, tricking them into making payments to the wrong accounts.
- Attorney impersonation: Attorney Impersonation sees attackers posing as legal representatives to manipulate business transactions, often during critical or high-stakes negotiations.
- Data theft: Data theft in BEC attacks focuses on stealing sensitive company data, which can be used for further attacks or sold on the black market.
Impact of BEC on businesses
- Financial losses: BEC attacks can lead to significant financial losses. For example, a single incident can result in the transfer of hundreds of thousands of dollars to fraudulent accounts, causing substantial financial strain.
- Reputational damage: Reputational damage from BEC incidents can be severe, leading to loss of customer trust and negative media coverage, which can affect a company’s market position and relationships.
- Legal implications: Legal implications of BEC include regulatory penalties and potential lawsuits from affected parties, which can add to the financial and operational burden on the business.
- Operational disruptions: Operational disruptions caused by BEC can interrupt business processes and workflow, leading to delays, reduced productivity, and increased recovery costs.
Detection and prevention of BEC attacks
Recognizing early warning signs of BEC is essential. These signs include unexpected requests for fund transfers, changes in communication style from executives, or urgent requests that bypass normal procedures. Training employees to recognize and respond to BEC threats is crucial. Awareness programs should cover topics like identifying phishing attempts, verifying email authenticity, and having solid standard procedure for reporting suspicious activities.
Best practices for email security
Implementing best practices for email security can help prevent BEC attacks:
- Multi-factor authentication: Adds an extra layer of security.
- Email filtering: Helps detect and block malicious emails.
- Regular software updates: Ensures vulnerabilities are patched.
Role of cybersecurity tools and services
Cybersecurity tools and services play a significant role in preventing BEC. These include:
- Email security solutions: To detect and block threats.
- Threat intelligence services: To stay updated on new attack methods.
- Incident response teams: To handle and mitigate attacks quickly.
Response and mitigation strategies for BEC
Steps to take immediately after discovering a BEC attack
After discovering a BEC attack, immediate steps include:
- Immediately isolate: Lock down affected accounts to prevent further compromise.
- Notify relevant stakeholders: Keeping everyone informed is essential, especially in possible security breach situations.
- Contact financial institutions immediately: In order to have the best chance of attempting to recover funds, time is of the essence here.
Incident response plans
An effective incident response plan for BEC should include:
- Preparation: Establishing protocols and response teams.
- Detection: Identifying and assessing the attack.
- Containment: Limiting the damage.
- Eradication: Removing the threat.
- Recovery: Restoring normal operations.
- Lessons learned: Analyzing the incident to improve future responses.
Collaborating with law enforcement and cybersecurity experts
Collaborating with law enforcement and cybersecurity experts is vital for a comprehensive response. They can provide:
- Investigation support: To track and apprehend attackers.
- Recovery assistance: To restore systems and data.
- Legal guidance: To navigate regulatory and compliance issues.
Recovery and remediation processes
Recovery and remediation processes should focus on:
- Restoring affected systems: To resume normal operations.
- Implementing additional safeguards: To prevent future attacks.
- Conducting a post-incident review: To understand the breach and improve defenses.
Future trends and developments in BEC
- Emerging BEC techniques:
- Deepfake technology: Using AI to create realistic but fraudulent communications.
- Advanced social engineering: Leveraging detailed personal information to craft more convincing attacks, especially when leveraged with uncensored AI Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Advancements in cybersecurity to combat BEC include:
- AI and machine learning: To detect anomalies and predict attacks.
- Blockchain technology: To secure transactions and communications.
- Enhanced encryption: To protect sensitive data.
Predictions for the future of BEC threats suggest increased sophistication of attacks, greater targeting of smaller businesses, and growing collaboration among cybercriminals.
Ensuring business continuity through vigilance
BEC is a significant cyber threat that can cause financial, reputational, legal, and operational damage to businesses. Understanding its workings, types, and impacts is crucial for effective prevention and response. Ongoing vigilance and adaptation to new threats are essential. Businesses must stay informed about emerging attack methods and continuously update their security measures. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including employee training, advanced security tools, and comprehensive response plans, is vital to protect against BEC and other cyber threats.