In this article, we discuss everything you need to know about how to change storage location of search index in Windows 10, including why you may want to consider it, some advantages, troubleshooting common issues, and best practices for Windows search index management.
Stop reacting—start leading. Learn how to shift to a proactive IT management strategy with our step-by-step guide. Get started.
What is Windows 10 search indexing?
The best (and simplest) way to think about Windows 10 search indexing is the Dewey Decimal Classification System, or the Library of Congress system, which libraries use to organize their collections systematically. Similarly, search indexing in Windows helps your computer sort through all your files, email messages, and other content so you can find results much faster.
When you first run indexing on your computer, it can take a few hours (or more) to complete, depending on how many files you have. After that, however, your computer learns to run indexing in the background, only re-indexing any updated data.
Windows search optimization
Having a digital index helps your computer find content much faster by looking for common properties, such as the date a file was created or having similar words or metadata. Typically, all properties of files are indexed, including file names and paths. This means that when you initiate a search, Windows search optimization refers to this index instead of scanning your entire drive, making the search process significantly faster and more efficient.
Indexing options in Windows 10
Your search index is stored on the system drive (usually the C: drive) by default. While this is convenient for the most part, it can lead to several challenges in the future if the system drive has limited free space or is heavily utilized. This may lead you to look for other indexing options in Windows 10, including how to relocate your search index.
Why should you relocate indexing files in Windows 10?
To be clear, performing a Windows 10 search index move is unnecessary if your computer runs smoothly and you do not have heavy resource requirements. That said, there are five reasons why you may want to relocate indexing files in Windows 10.
- Freeing up space on the system drive: The primary reason you may be searching for how to optimize search indexing in Windows 10 is to free up space on your system drive. Moving the search index to another, less utilized drive can dramatically improve overall system performance. It’s worth noting that a nearly full drive can slow down operations or prevent updates (or processes like patch management) from being installed or performed.
- Enhancing system performance by moving the index to a faster or less utilized drive: Reducing competition for system drive resources can improve overall system responsiveness. This allows your computer to operate much more optimally, such as performing necessary security scans and detecting vulnerabilities. (Pro tip: Drives with higher read/write speeds like SSDs are particularly suitable for when you need to move your search database in Windows 10).
- Avoiding storage conflicts: Relocating your Windows 10 search index prevents storage issues or failures. This is essential for systems with smaller storage drives. In addition, moving the index to a secondary drive can help reduce wear on the system drive, potentially prolonging its lifespan.
- Customizing storage preferences: Users with complex storage setups, such as those using RAID storage or network-attached storage (NAS), may prefer to keep the index on a specific volume for better organization and easier management.
- Reducing backup times: If your system drive is frequently backed up, excluding the search index from this drive can reduce backups and save storage space on backup devices (Pro tip: We recommend NinjaOne Backup regardless of your backup preferences to secure your business-critical data confidently).
Step-by-step guide: Changing the storage location of the search index
Before proceeding, ensure the following:
- Backup important data: Create a backup of critical files to avoid any data loss.
- Ensure adequate permissions: Verify that you have administrative rights to change system settings and that the target drive has sufficient storage capacity.
- Check new location accessibility: Confirm that the new location will remain accessible during system operation.
Once you’ve completed these steps, we now go to the actual change of search index location in Windows 10.
Option 1:
1. Access indexing options
a. Open the Control Panel and navigate to “Indexing Options”. You can also use the Search function at the upper right-hand corner to access this faster.
b. Click “Advanced” to access advanced settings.
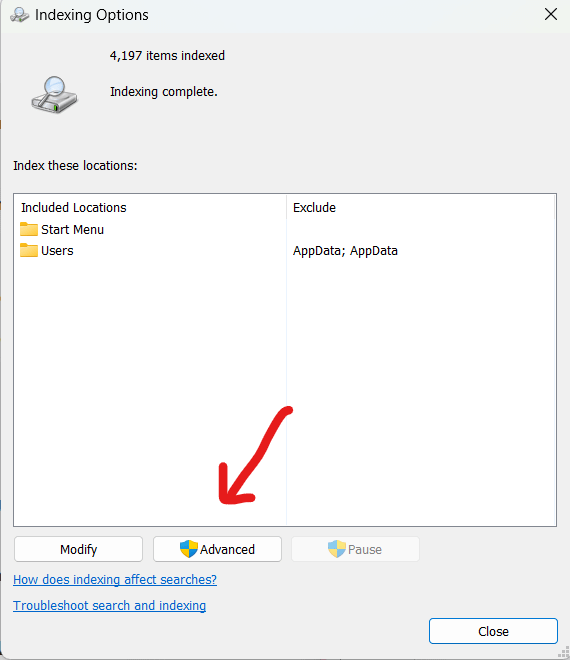
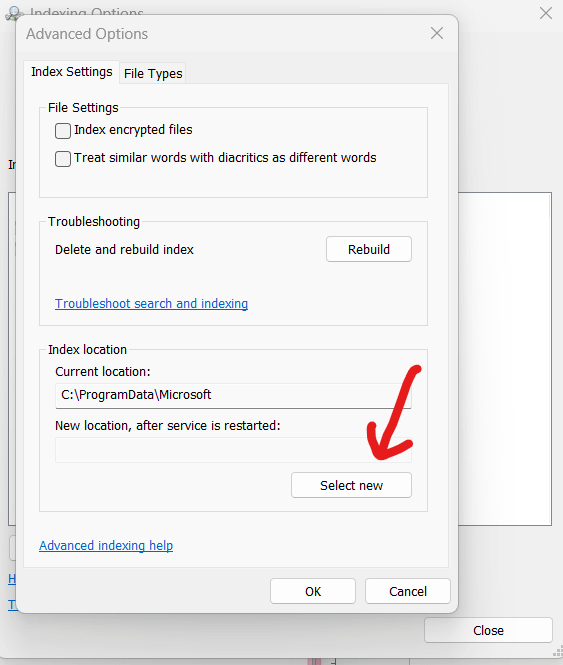
2. Relocate the search index location
a. Click on the “Select New” button under “Index Location” .
b. Select the new location you want for the index data files and click “Ok”.
c. Click “Ok” again to apply the change.
d. Click “Close”.
Option 2:
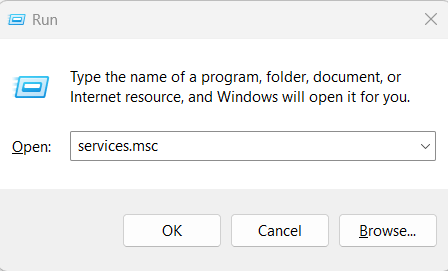
1. Stop the Windows search services
a. Simultaneously press “Win + R”.
b. Type “services.msc” and press “Enter”
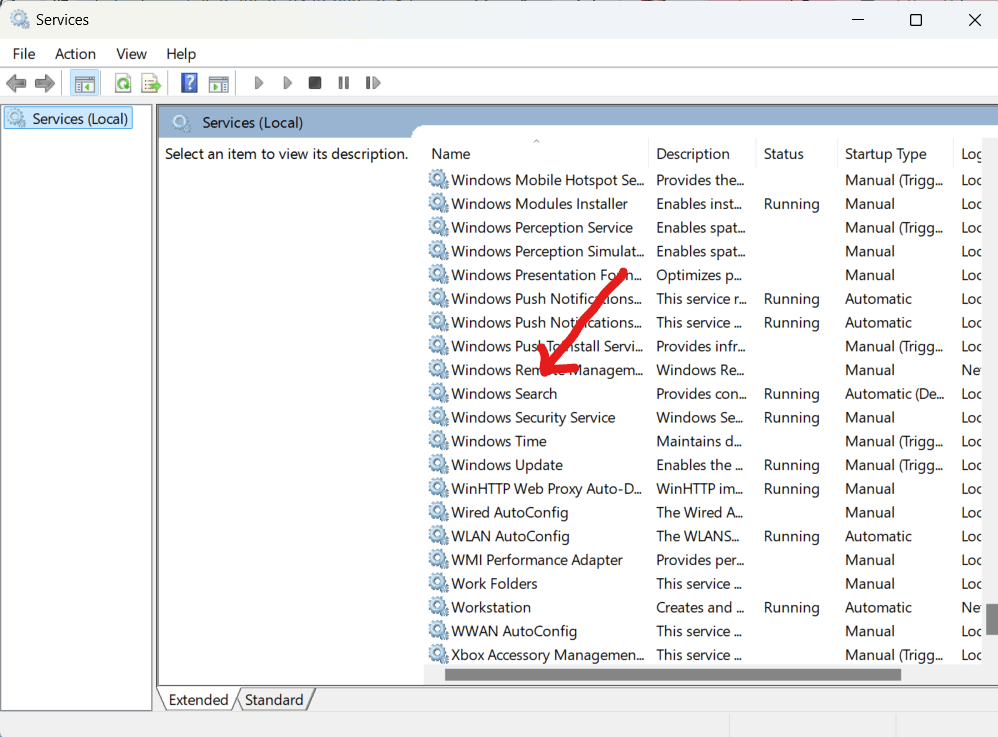
c. Locate “Windows Search” in the list of services.
d. Right-click and select “Stop” to temporarily halt the service.
2. Relocate the index file
a. Follow steps 1 and 2 in Option 1.
b. Click “Ok” to save changes.
3. Verify and restart
a. Restart the Windows Search services by returning to “services.msc”, right-clicking “Windows Search” again, and selecting “Start”.
b. Windows will begin rebuilding the index in the new location.
Troubleshooting common issues
What to do if the index fails to move or rebuild correctly
This typically happens when the new location is inaccessible during the transfer process or has insufficient space. If the index fails to move or rebuild, verify that the drive is properly connected and not in a read-only state.
If the problem persists, try:
- Restoring default settings: Return to indexing options, restore the default location, and follow the above steps.
- Repair system files: Sometimes, changing index locations may not occur if you have damaged files. In this case, go to “Command Prompt” and input the command, “sfc /scannow” to check and repair files.
Solutions for permission errors or inaccessible drives
This occurs when the new location is not given sufficient access rights. To resolve this:
- Grant full control: Go to “Home” and look for your target location in the left-hand corner. Right-click this location, go to “Properties,” and select “Security”. Ensure your user account has full control.
- Run as administrator: Make sure that you perform all actions as “administrator”.
- Check drive accessibility: For network drives, verify that the drive is mapped correctly and remains connected.
Tips for optimizing the new index storage location
To minimize common issues, make sure you choose a fast drive, such as an SSD or a high-performing HDD, for better indexing speeds. It’s also important that this alternative drive is not heavily utilized as well—or your Windows search optimization may not be as effective as possible.
We also recommend that you carefully plan your Windows 10 search index move properly. If you’re using a traditional HDD, for example, consider defragmenting the drive to improve its read/write speeds. In addition, maximize tools to ensure the drive’s health and performance remain optimal.
Best practices for search index management
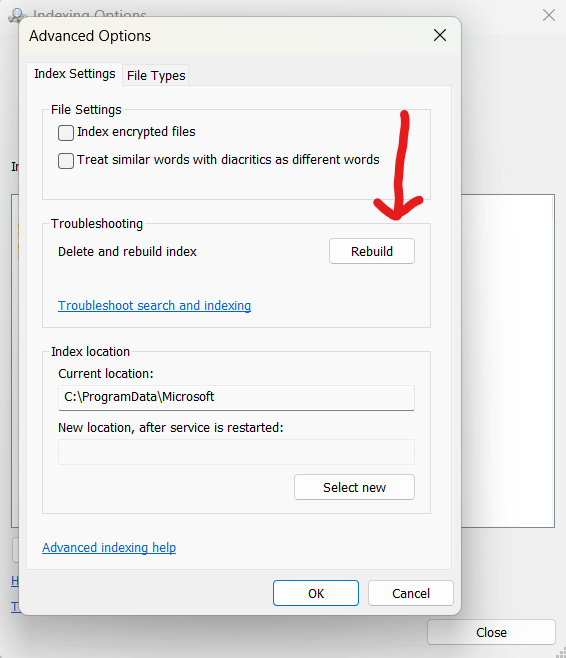
- Regular maintenance: Rebuild the index periodically to ensure it remains efficient and free from corruption. You can do this by accessing “Indexing Options” from the Control Panel and selecting “Rebuild” under Advanced Settings.
- Monitor performance: Keep an eye on system performance after relocating the index. Use tools like Task Manager to check for excessive CPU or disk usage by the search indexing process. Adjust indexing options in Windows 10 as needed.
- Limit indexed locations: Review and limit the locations indexed by Windows Search to only those necessary.
- Exclude unnecessary file types: It’s a good idea to exclude those not frequently searched or required. In “Advanced Options,” you can customize the indexed file types.
- Use reliable drives: Make sure that the drive you intend to use when relocating indexing files in Windows 10 is stable and has sufficient free space.
- Backup index location: The importance of backing up your files periodically cannot be overemphasized. While rebuilding the index is always an option, backups can save time in case of data corruption, loss, or breach.
- Revert if necessary: If issues persist or performance does not improve, it may be wisest to revert the index to its default location and perform the abovementioned steps.
Properly change search index location in Windows 10
If you’ve been searching “How to optimize search indexing in Windows 10”, you may have come across several guides that detail the “how” of the process but not the “why” or the “what ifs” that may happen once you relocate the search index.
This article provides a more holistic and comprehensive overview of changing the storage location of the search index in Windows 10. By following this guide and adhering to best practices, you can safely and effectively manage your search index to optimize your system’s functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is it safe to change the search index location?
Yes, it is safe to change the search index location. We recommend following the steps outlined above to reduce risks.
2. Can the search index be moved to an external drive?
Yes, but it’s generally not recommended. External drives may not always be connected to your computer, which may lead to search functionality issues.
3. Will this impact Windows search performance?
Relocating the index to a faster, less utilized drive can enhance performance and contribute to higher operational efficiency. Moving it to a slower drive may have the opposite effect.