This guide demonstrates how to modify system restore point frequency in Windows 10 as well as in Windows 11. It includes an explanation of how Windows system restore behaves, and how to change system restore point settings to change the creation interval using the Command Prompt/PowerShell or the Windows Registry Editor. This tutorial also provides instructions for creating system restore points using the Windows Task Scheduler.
Understanding system restore point creation in Windows 10 and Windows 11
System Restore is a part of the Windows System Protection feature, available in all versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11. It takes periodic snapshots of your Windows OS and settings (including drivers and the registry), allowing you to roll back to a previous version. This is vital for restoring a functional system if Windows Update fails to install correctly, a driver update leaves your system unable to boot, or to reverse the effects of a malware infection.
It does this by creating “restore points” that capture all the required files and configurations, so that they can be restored from the Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE).
Windows System Protection (including System Restore) is not enabled by default, and must be enabled in the Control Panel.
Why change the frequency?
Windows automatically creates system restore points on a schedule, and you can also manually create them yourself. System restore doesn’t affect the files located in your user profile directory.
By default, a system restore point is created at a frequency of every seven days, or whenever a Windows update, driver, or program is installed. A restore point is only created automatically, on a schedule, or via a command if one hasn’t been created in the last 24 hours. Manual system restore points can be created whenever required, regardless of when the last one was created.
There are several reasons why you may wish to alter the system restore point creation schedule:
- To create more frequent snapshots if you regularly make changes to your system, ensuring there is always a recent good state to revert to.
- To reduce the frequency of restore point creation so that less disk space is used or if the process is interrupting other tasks.
How to modify system restore point creation interval
There are several methods you can employ to change system restore point creation frequency in Windows. Before you attempt any of the below methods, you should make a backup of your system.
Note that none of these methods restrict how often you can manually create system restore points.
Method 1: Using the Windows Registry to set system restore point timing
Before you make modifications to the Windows registry, you should make a backup of it.
To modify system restore point creation frequency using the Windows Registry, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and select Run
- In the Run dialog, enter regedit and click OK
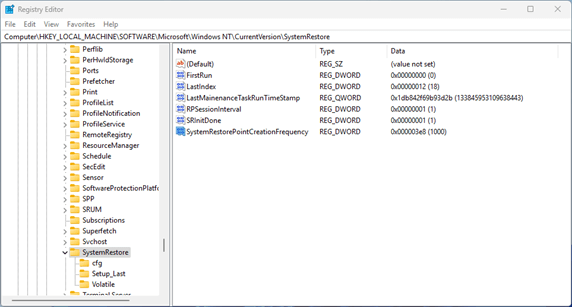
- Navigate to Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore (you can copy and paste this path into the navigation bar in the Registry Editor)
- Double-click on the SystemRestorePointCreationFrequency DWORD value, set the Base to Decimal, and the Value data to the number of minutes you want to set the minimum system restore point creation interval to (to disable the frequency restriction, set this value to 0)
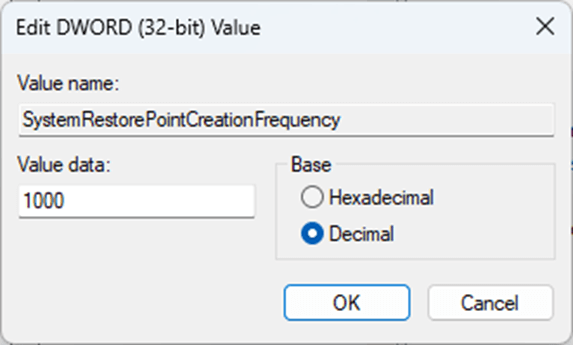
If the SystemRestorePointCreationFrequency does not exist, right-click in a blank spot under the existing registry keys, and select New > DWORD (32 Bit) Value, giving it the name SystemRestorePointCreationFrequency.
Method 3: Using the Command Prompt to always create a restore point
Run the following command in an elevated Command Prompt or PowerShell session. This command sets system restore to avoid skipping on creating a restore point, even if one has been created in the last 24 hours:
REG ADD “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore” /V “SystemRestorePointCreationFrequency” /T REG_DWORD /D 0 /F
This will create the SystemRestorePointCreationFrequency registry value detailed above, and set its value to 0. You can then modify this value using the Registry Editor using the steps above.
To undo this change, run the following command to delete the registry value:
REG DELETE “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore” /V “SystemRestorePointCreationFrequency” /F
Method 3: Using Task Scheduler to create system restore points
Alternatively, you can use the Task Scheduler to create system restore points on your own custom schedule, removing the need for using the registry editor or command line:
- Open the Windows Task Scheduler from the Start Menu
- Click on Task Scheduler Library in the left navigation pane
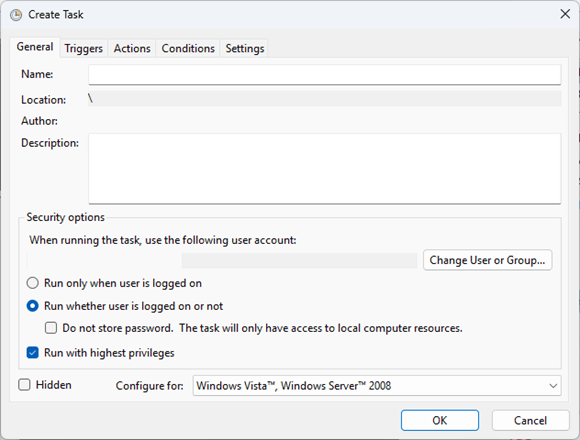
Select Action > Create Task… from the toolbar - Name the task “Create system restore point”
- Check the Run with highest privileges checkbox and enable the Run whether user is logged on or not option
- In the Actions tab, select New… and enter powershell.exe in the Program/script field
- In the Add arguments (optional) field enter the following command, including the quotes:
“-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command “Checkpoint-Computer -Description “Restore Point (Automatic)” -RestorePointType “MODIFY_SETTINGS”””
- Press OK to save the action
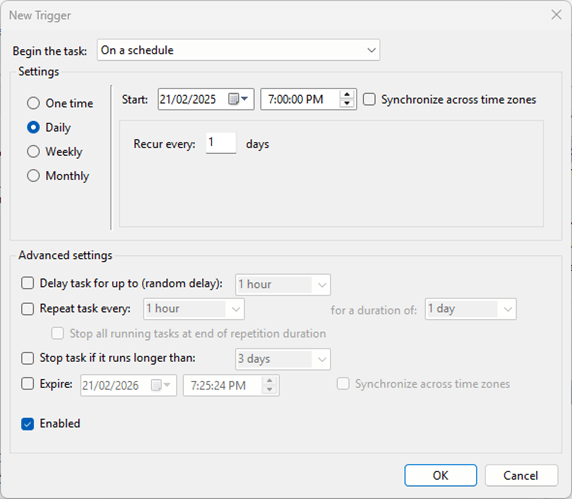
- In the Triggers tab click New… and then set your schedule, making sure the Enabled checkbox is checked
- To avoid creating system restore points while you’re using your Windows PC, or while it is on battery power, you can specify this in the Conditions tab
- Press OK to complete creating the scheduled task, and when prompted, enter the user credentials that the task will run as to ensure it has the necessary permissions.
Managing the backup and restoration of fleets of enterprise devices
Restoring Windows system, driver, and registry data is only one part of recovering from malware attacks, hardware failure, and other events that cause data loss.
NinjaOne Backup gives you the tools to back up all of your data from your IT infrastructure and end-user devices and restore it lightning-fast, reducing downtime and protecting your vital business data against ransomware attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I change the restore point creation interval in Windows?
You can modify system restore point settings in the Windows Registry at the location Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore.
How often does Windows create a system restore point?
By default, Windows creates system restore points every 7 days, or when manually triggered. Restore points are not automatically created if one exists from the last 24 hours.
How can I fix Windows system restore points not being created?
System restore points are only created when System Protection is enabled.
How can I create system restore points automatically at a set time?
The Windows Task Scheduler can be used to set a custom schedule for the creation of system restore points.