This guide demonstrates how to remove file property details in Windows 10 and Windows 11. It includes instructions explaining how to add, change, and remove file properties (also known as metadata). This allows you to edit or remove sensitive metadata such as geolocation data, file author name, as well as other information such as title, tags, and comments, so that files can be safely published online or shared with third parties.
How to view file property details in Windows 10 and Windows 11
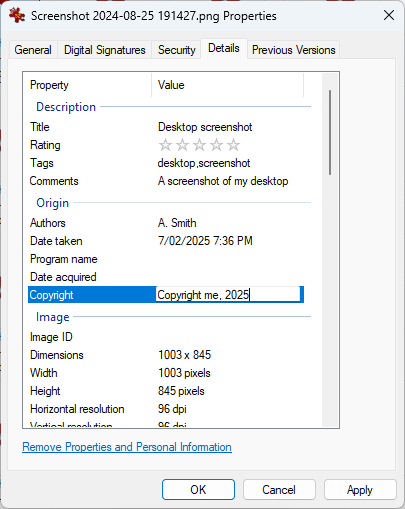
To view a file’s metadata using file property details, right-click on the file, and select Properties. You can then click on the Details tab in the file property window to view the file’s metadata. If the format of the selected file does not support metadata, only basic information will be displayed such as the files path, size, type, and creation/modification dates.
Note that you can view the file property details of multiple files. If the files share a property, it will be displayed, but if the values differ that property will instead display (multiple values) rather than listing the value for each file.
How to configure file property details
When viewing file property details in the Windows Explorer Properties dialog, you can also configure file property details by clicking in the Value field and adding or updating the information stored there. To save your changes, make sure you press the Apply or OK button.
Note that you cannot create new Property fields to add custom metadata, as they are defined by the file format — you can only add information to the fields provided.
How to edit file metadata for sharing in Windows
Editing the file property details effectively adds, edits, or removes the metadata for sharing, even when the file is transferred to other operating systems or uploaded online. You can also use third-party tools to edit file metadata. For example, ExifTool can modify metadata of image files, and VLC Media Player can be used to edit the metadata of audio and video files.
How to remove personal information using file property details
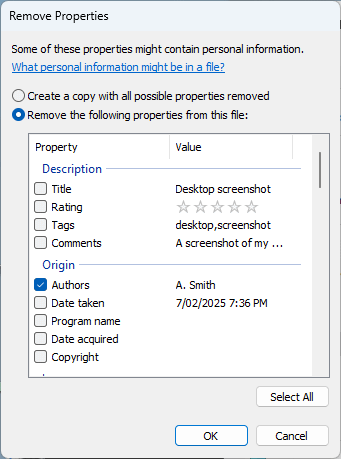
Windows 10 and Windows 11 include the ability to redact file metadata, allowing you to easily remove personal information or other sensitive metadata from them. To do this, open the file properties and navigate to the file properties Details tab, and click Remove Properties and Personal Information.
From here, you can either choose to create a copy of the file with all properties removed, or remove specified properties from the current file without creating a copy (resulting in the permanent loss of that information). Clicking OK to confirm will immediately remove the selected properties.
Note that it’s possible to perform this with multiple files selected to batch-remove metadata.
Understanding file property details
In Windows, file property details show you the metadata included with a specific file. This can include information such as the creator of the file, and their organization details. For some files such as photos, this also includes EXIF data that specifies the location the photo was taken and information about the device used.
This information is highly useful when organizing and searching for files (for example, being able to find documents by their author and photos by the time and location they were taken), but it can raise privacy concerns if these files need to be shared.
Common file types that support editable metadata include:
- Image files, including TIFF, RAW, HEIC, JPEG and PNG images
- Audio files, including MP3, FLAC, WAV, AAC, and OGG formats
- Video files, including MP4, AVI, MOV, and WMV
- Microsoft Office files including Word, Excel, and PowerPoint documents
Use cases and benefits of managing file metadata
Using the Windows feature to create a copy of a file with all metadata removed is a quick way to make it safe for sharing online.
However, if you are sharing the file for professional use, you may wish to specify exactly which metadata to remove (and which to keep). For example, it may make sense to retain color information in photos and videos being shared with your colleagues for editing, or in documents to make it easier to search for them using their metadata.
Managing the safe sharing of sensitive metadata in the enterprise
It is becoming increasingly important to restrict what information employees have access to. Managing access to files, including those with sensitive metadata, is critical for compliance with privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, and for protecting sensitive business information.
NinjaOne provides a complete remote monitoring and management (RMM) solution that lets you monitor employee devices for suspicious activity, and securely manage your Windows, Apple, Android, and Linux devices, as well as user accounts and file permissions, from a single web interface.
FAQ
Why can’t I edit metadata for some files?
Metadata can be stored in a number of ways, and not all of them are directly editable using Windows built-in tools. Some files embed their metadata inside the file (for example, RAW image formats), while some store it in an extra separate file. It also may not be possible to edit the metadata of new or uncommon file formats that are not readable by Windows. Additionally, audio and video files with DRM (digital rights management) do not allow some of their metadata to be edited.
You will also need to make sure you are logged in with a user account with the correct permissions to modify the required files.
Can I restore removed metadata?
No, editing and removing metadata from a file is permanent. You cannot restore metadata that has been removed or edited without restoring the unedited file from a backup.
What’s the best tool for bulk metadata changes?
Windows 10 and Windows 11 provide convenient built-in tools for modifying file metadata in bulk. However, if the files you are trying to edit are in an unsupported format, you will need to research the specific tools required to read and edit their metadata. This may require PowerShell scripting to do so in bulk.