This guide offers step-by-step instructions demonstrating how configure USB selective suspend in Windows 10 as well as in Windows 11. It also includes an explanation of USB selective suspend, and the impacts of altering USB selective suspend settings. This will help you troubleshoot USB issues in Windows, and control USB device power management on Windows PCs.
What is USB selective suspend?
USB selective suspend is a power management feature in Windows 10 and Windows 11 that sets individual USB ports to a low-power state (or a suspended state), without affecting other USB ports located on the same hub.
This allows Windows to save power by suspending individual ports for devices that aren’t in use, which both improves the overall energy efficiency of devices, as well as improves the battery life of laptops and tablets. As many USB devices like mice and scanners do not need full power constantly, they can be safely suspended until the user interacts with them.
When a USB port is suspended using selective suspend, it is automatically resumed (returned to full-power mode) when it is required. For example, when the user moves their mouse, it will be resumed from selective suspend so that it has enough power to record and transmit mouse movements.
When should you enable or disable USB selective suspend?
USB selective suspend should be enabled on your Windows 10 or Windows 11 system by default.
USB selective suspend will behave differently depending on the kind of device. For example, external hard drives will stop spinning when suspended (increasing the time it takes to access them as they need to spin back up when resumed), and web cameras may take a moment to ‘wake up’ and start recording after being in a suspended state.
Most of these delays are not noticeable to the user, and USB power management is generally best handled automatically by Windows.
However, there are some specific scenarios where you may want to enable or disable USB Selective suspend: when you’re using older devices that do not properly support being suspended, or when the suspend/resume process interferes with sensitive devices where timing is important (such as sensors, or gaming mice).
Step-by-step guide: How to turn on or off USB selective suspend
There are several methods for enabling and disabling USB selective suspend for all devices on your Windows PC.
Windows 10: Using Power Options to disable USB selective suspend for all devices
- Right-click on the Start button and select Settings
- Select System and then Power & Sleep
- Click on Additional Power Settings
- Select Change Plan Settings next to your Power Plan
- Click Change advanced power settings
- Expand USB Settings > USB selective suspend
- Change the Setting value to either Enabled or Disabled
Windows 11: Using Power Options to disable USB selective suspend for all devices
- Right-click on the Start button and select Run
- Enter control in the Run dialog and press the Enter key
- Select Power Options from the Control Panel
- Select Change Plan Settings next to your Power Plan
- Click Change advanced power settings
- Expand USB Settings > USB selective suspend
- Change the Setting value to either Enabled or Disabled
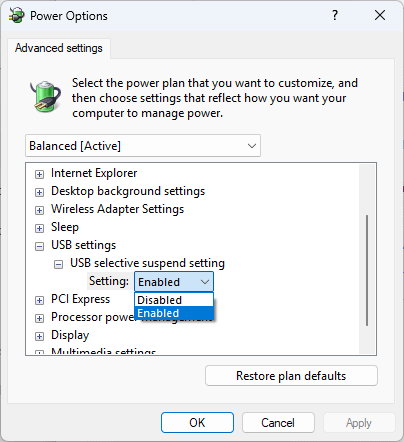
Note that in both Windows 10 and Windows 11, you may need to click on Change settings that are currently unavailable when prompted, and enter the details of an Administrator account.
FAQ
What devices are affected by USB selective suspend?
USB selective suspend is enabled by default for all supported devices. This includes input devices (mice, keyboards), storage devices (hard drives, flash drives), multimedia devices (cameras, printers, scanners), and communication devices (modems and Wi-Fi adapters).
Can turning off USB selective suspend damage hardware?
Disabling USB selective suspend will not damage devices, but may impact their longevity. For example, a portable USB hard drive that is not suspended when idle, and continues spinning its mechanical parts, will have increased wear over a device that is suspended and resumed only when needed. This wear will reduce the lifespan of the device.
How can I troubleshoot issues caused by USB selective suspend?
If a device has an intermittent problem, you can check if USB selective suspend is the cause by disabling it and seeing if the malfunction continues. If the issue is resolved, you can then disable it for that specific device using the Device Manager.
When USB device issues persist, you may need to update your device drivers or replace faulty hardware.
Device and power management in enterprise environments
Enabling or disabling USB selective suspend can help troubleshoot USB issues and improve power efficiency. For IT departments that manage fleets of devices, USB power management and troubleshooting using the manual steps detailed above is both time-consuming and cumbersome.
Endpoint management by NinjaOne puts all of your devices’ configurations in a single unified web interface. Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices, as well as Apple and Android mobile devices can all be centrally monitored and managed, with remote support and troubleshooting. Rather than manually altering USB power settings in Windows per-machine, you can automate and deploy configurations based on the USB devices your employees use, and their requirements.