In this guide, we discuss the steps on how to delete saved RDP credentials. RDP, which stands for Remote Desktop Protocol, is a powerful feature in Windows that allows users to remotely access another computer over a network. As you can imagine, it’s highly useful for hybrid workforces or any IT enterprise that needs to manage remote systems.
Nevertheless, RDP may introduce security risks if not used correctly. Managing stored credentials is crucial to prevent unauthorized access, enhance security, and resolve login issues.
Enable or disable RDP on workstations using PowerShell.
Steps to clear saved passwords in Windows Remote Desktop
We’ve listed 5 options on how to remove Remote Desktop credentials.
Option 1: Using Windows Credential Manager
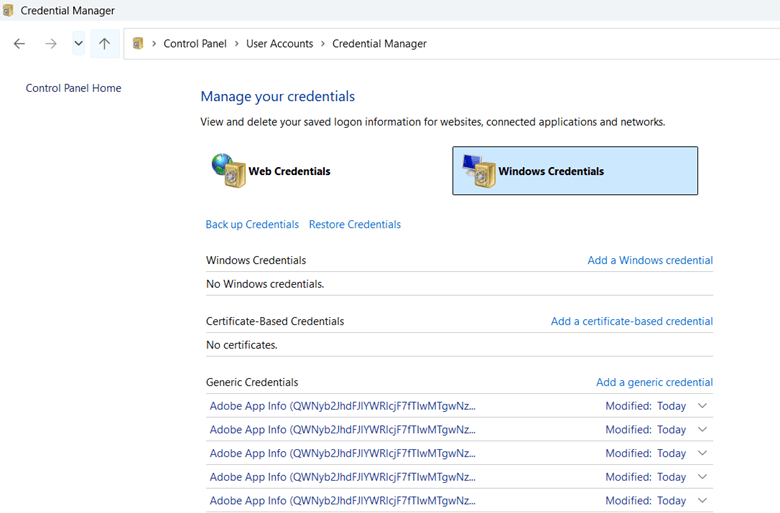
Windows Credential Manager is the most user-friendly method for deleting saved RDP credentials. Follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to Credential Manager.
- Click on Windows Credentials to display a list of stored credentials.
- Locate the entry corresponding to your RDP connection. These credentials are usually labeled as TERMSRV/ followed by the remote computer’s name or IP address.
- Click on the credential entry to expand it, then select Remove.
- Confirm the deletion when prompted.
With this method, you will be required to enter new credentials the next time you attempt to connect to the remote machine.
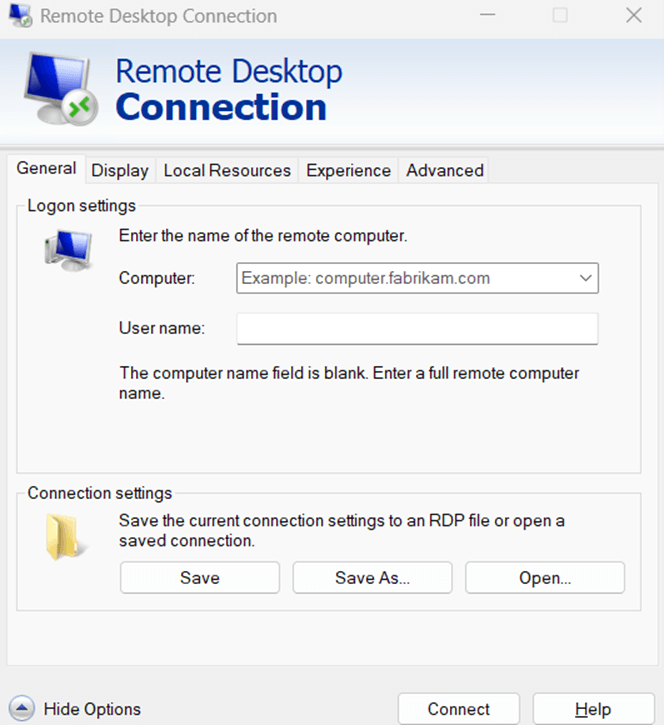
Option 2: Using the Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) interface
The RDC client provides a direct way to delete saved credentials. Here’s how:
- Press Win + R, type mstsc, and press Enter to open the Remote Desktop Connection client.
- Click on Show Options at the bottom left.
- Under the General tab, locate the User name field where the saved credentials are stored.
- Click Delete Credentials (if available).
- Close and restart RDC to ensure changes take effect.
If the “Delete Credentials” button is not visible, use Credential Manager as an alternative method.
Option 3: Modifying Group Policy Settings (for IT admins)
Administrators can enforce policies to prevent Windows from storing RDC credentials altogether. This method is ideal for securing enterprise environments.
- Open Group Policy Editor by pressing Win + R, typing gpedit.msc, and pressing Enter.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration → Administrative Templates → System → Credentials Delegation.
- Locate and double-click Do not allow passwords to be saved.
- Select Enabled, then click Apply and OK.
- Restart the system so that changes take effect.
By enabling this policy, users will always be required to enter credentials manually when connecting via RDC.
Option 4: Deleting credentials via Windows registry (for advanced users)
For advanced users, stored RDC credentials can be removed from the registry.
- Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers
- Expand the Servers key and locate the subkey corresponding to the remote computer.
- Right-click the subkey and select Delete.
- Close the Registry Editor and restart the computer.
⚠️ Caution: Editing the registry carries risks. Always back up the registry before making modifications. Use a tool like NinjaOne to back up business-critical data.
Understanding saved credentials in Remote Desktop
When a user logs in to a remote desktop session and chooses to save their credentials, Windows securely stores these credentials for future use. This allows users to connect without re-entering login details. However, saved credentials are stored in locations that, if compromised, pose a security risk.
Windows primarily stores RDC credentials in two locations:
- Windows Credential Manager: This tool manages stored passwords for various Windows services, including RDC.
- Windows Registry: Advanced users may find stored RDC credentials in the registry, particularly under Terminal Services keys.
Leaving old or unused credentials stored can be a security vulnerability, especially on shared or corporate systems. Threat actors can exploit these vulnerabilities and gain access to a compromised system. As such, regularly managing and removing saved credentials is a best practice in any robust credential management strategy.
Run scripts on Windows or Mac using any custom credentials.
→ Learn more about NinjaOne’s Credential Exchange.
8 best practices for secure Remote Desktop management
The most common cyberattacks exploit weak or improperly stored credentials. That is why IT experts continue to stress the importance of enforcing strong security measures. Regular audits, password policies, and proper session management can help safeguard sensitive remote connections. Below are eight best practices to follow for secure Remote Desktop credential management:
- Remove Remote Desktop credentials regularly: Periodically clear stored RDP passwords to ensure security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Use strong, unique passwords: Always use complex passwords for RDC accounts to reduce the risk of credential theft.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Adding MFA significantly enhances security by requiring an additional verification step.
- Audit and monitor stored credentials: Regularly review stored RDC credentials and delete Remote Desktop saved login details that are no longer needed.
- Disable automatic credential saving: Use Group Policy settings to prevent Windows from storing Remote Desktop Connection credentials automatically.
- Implement session timeout policies: Configure timeouts to automatically disconnect idle remote sessions.
- Use PowerShell for bulk credential removal: Automate Remote Desktop Connection credentials removal using PowerShell for efficiency in enterprise environments.
- Regularly update Windows and security settings: Ensure all security patches and updates are applied to minimize vulnerabilities in RDC.
Deleting saved RDP credentials
Managing stored RDC credentials is crucial for maintaining security and troubleshooting connection issues. This guide has outlined multiple methods to remove saved credentials, ranging from simple GUI-based methods to advanced registry modifications and automation through PowerShell. By following best practices, you ensure your RDC sessions remain secure and free from unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What happens if I delete my saved RDC credentials?
When credentials are deleted, you will be required to enter your username and password the next time you connect to the remote machine.
2. Can I disable credential saving entirely in Remote Desktop?
Yes, you can prevent users from saving RDC credentials using Group Policy Editor.
3. How do I clear credentials for multiple remote desktops?
You can systematically remove credentials for multiple remote desktops using PowerShell or Credential Manager.