Cybersecurity is a constant balancing act: We must proactively defend our companies from existing threats while predicting what threat actors could do in the future. We also need to consider the practicality of our strategies and IT budget to manage and thrive in this rapid digital transformation.
Considering that only 15% of organizations are optimistic that cyber skills and education will significantly improve in the next two years (World Economic Forum, Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2024), it is essential that your MSP or IT enterprise perform regular IT security audits to ensure that there are no gaps in your existing security strategy.
That’s where we come in. We’ve written this comprehensive guide on the best IT security checklist to protect your business. When performing your IT security audits, you can go through the IT security checklist to ensure that you’ve crossed all the “ts” and dotted all the “is” and protected your organization as much as possible from various cyber threats.
🖥️ Harden your defenses against cyberattacks.
Table of Contents
- The importance of security risk assessment
- What are the advantages of using an IT security checklist?
- How do I make an IT security checklist?
- Securing your asset: Creating your IT security checklist
- Device/Endpoint security
- Network security
- Application security
- Data security
- User security
- Protecting your assets: Defining the functions
- Identify
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
- Cybersecurity best practices
- How NinjaOne supports your IT security checklist
The importance of security risk assessment
Simply stated, there are many threats to IT systems, from malware to human error. While conventional wisdom would have us believing hackers are the sole source of potential problems, we fail to recognize the vulnerabilities that become present with insider threats, poor data governance, or other factors that determine data integrity.
The stakes are high for cybersecurity, regardless of whether you are in the IT industry or any other sector.
- From a threat landscape perspective. Each day, criminals become more sophisticated and look for ways to exploit vulnerabilities in your organization. In fact, experts predict that the cost of cyber attacks on the global economy will reach $10.5 trillion by the end of 2024 (Forbes).
- From an information security perspective. Data is arguably the most valuable asset today—and hackers want to steal it (usually by ransomware) to gain a significant advantage over you. This explains why Gartner experts recommend that CISOs invest in several tools that build data resilience and deploy vulnerability management (Gartner, Top Eight Cybersecurity Predictions for 2024).
- From a software vendor perspective. MSPs and MSSPs are highly encouraged to work with a software vendor that offers end-to-end protection for the entire IT network. If possible, look for a software provider that leverages automation to free up your IT technicians so they can focus on more high-value, strategic projects.
Still unconvinced? Let’s look at some numbers.
- The global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $13.82 trillion by 2028 (Statistica). This includes data damage and destruction, lost productivity, intellectual property theft, fraud, and hacked data, among other things.
- Organizations with an incident response team and the proper IT security checklist can save around $1.5 million in data breach costs compared to businesses without these audits (IBM).
- The Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Agency (CISA) recently released 21 industrial control system advisories just for July 2024 alone about the various security issues, vulnerabilities, and exploits currently surrounding the IT industry.
Performing an IT security risk assessment allows you (or a third party) to examine your systems, processes, and technologies to identify risks in your environment that a threat actor could exploit
During the evaluation, tools are used to do a vulnerability assessment against your network. This assessment includes pen testing, auditing user behavior, and faking phishing attempts. Once those vulnerabilities are identified, a report listing the vulnerabilities is generated. Then, your organization can remediate them. The IT security risk assessment report provides concrete facts and evidence of what is lacking in your organization’s cybersecurity.
An IT security checklist helps you safeguard your organization from threats.
Develop better cyber hygiene with this free guide on the top 5 IT Security Fundamentals.
What are the advantages of using an IT security checklist?
Using an IT security checklist helps to ensure that all your bases are covered and your IT environment is protected. By addressing every component, you leave no stone unturned and protect all components of your technology against cyber threats. Check out this IT security checklist to learn what basic elements to include in your IT security strategy:
How do I make an IT security checklist?
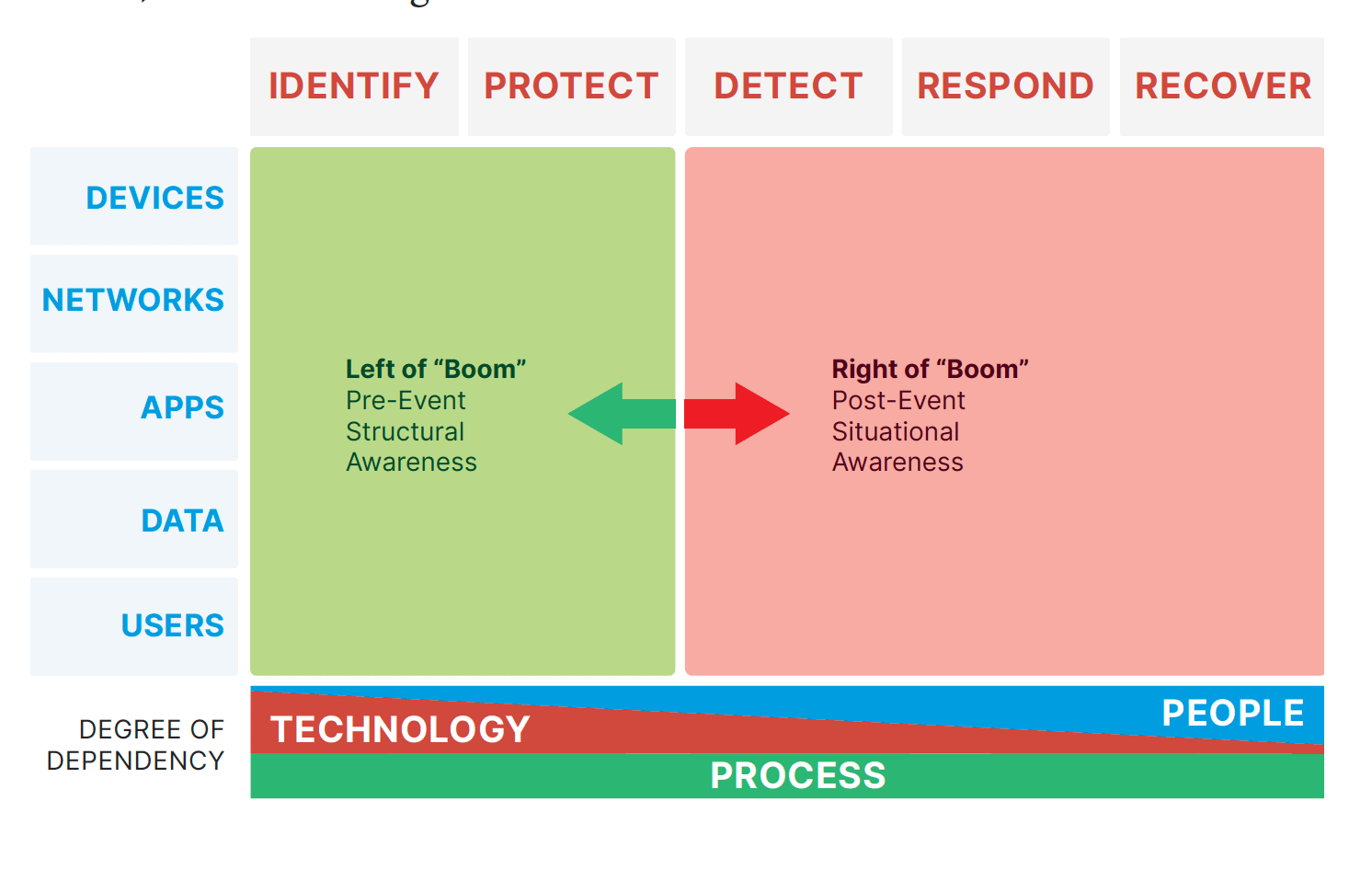
We recommend following the Cyber Defense Matrix, first developed by Sounil Yu and inspired by the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. This 5×5 grid helps IT professionals expertly navigate the cybersecurity landscape. It looks something like this

As you can see, the grid comprises two dimensions: function and assets. Your organization must adequately respond to each intersection to achieve the best IT security.
Let’s break these concepts down further.
ASSETS
| Devices | Apps | Networks | Data | Users | |
| Describes/Covers | Workstations, servers, phones, tablets, etc.
Check out this guide on endpoint devices for a full list. |
All software (and their interactions). You can also count other applications in your IT network, including any integrations your IT enterprise uses. | Any connections flowing between or among devices.
Consider creating a network topology to help identify your networks’ various elements. |
Content at rest, in transit, or in use.
You can read a more in-depth guide of data at rest here. |
Any person using any of these assets. |
FUNCTIONS
| Identify | Protect | Detect | Respond | Recovery | |
| Describes/Covers | Make an inventory of all your assets. If possible, include any metric of their attack surfaces, baseline cybersecurity resilience, and risk assessment. | How does your organization currently prevent or limit the impact of cyber threats? This includes patch management, endpoint hardening, vulnerability mitigation, etc. | Determine how your company discovers incidents or threat events. | How do you respond to these events found in “Detect”? | What processes are in place to return to normal operations? This includes your disaster recovery plan. |
Below the grid, there is the degree of dependency. This displays a continuum of how much technology or people each function depends on. The identified function relies the most on technology. As you move to the right on the grid, each function depends on it less, while each consecutive function’s dependency on people grows. Under the technology and people continuums, there is a constant dependency on the process.
It’s important that you have the necessary people, technology, and processes in place to perform each of these functions.
Securing your assets: Creating your IT security checklist
Before going through each asset and its specific checklist, it’s worth noting that some strategies may overlap. This is why most IT experts recommend working with a trusted software vendor that provides most of the required capabilities.
Additionally, while we tried to be as thorough as possible, these checklists should not be considered hard-and-fast rules. Feel free to adjust them to suit your specific needs and budget.
1. Device/Endpoint security
Device or endpoint security aims to protect your systems and assets on the devices or endpoints. If these assets were leaked or compromised, they could majorly impact your organization. Endpoint security controls include controlled access, drive encryption, password management, managed AV, and device approval.
Considerations for your endpoint security checklist
- Asset discovery and inventory. You need real-time information about your endpoints and all software installed in each one. Strong endpoint security always begins with identifying every device across your entire IT estate. This visibility helps you easily detect and remediate any performance issues.
- Patch management. Installing the latest software versions on your devices keeps your IT network healthy. NinjaOne, rated #1 in patch management, simplifies this process by automating each step so you can focus on other tasks.
- Vulnerability scanning. You must regularly scan your devices for vulnerabilities. This is especially important if you manage multiple devices.
- Real-time threat response. How do you minimize the impact of detected threats? Your IT security strategy must have several protocols to reduce business disruptions.
- Managed endpoint security. It may be more cost-effective to work with an endpoint management vendor like NinjaOne to safeguard your devices. That said, if you prefer to do this on your own, ensure that you can identify and monitor your endpoints, properly manage your policies and updates, and respond to threats as soon as possible.
Endpoint hardening is an essential practice in any IT security strategy.
Download this free endpoint hardening checklist to reduce your attack surface.
2. Network security
Your organization’s network provides access to all elements of the IT infrastructure, so it is crucial to implement effective network security. This is accomplished through network segmentation, access control, sandboxing, and zero trust.
Considerations for your network security checklist
- Access control. Ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive information. This is part of your network access control (NAC) and ensures the security, compliance, and integrity of your network by enforcing rules that determine who can access what data point at any given time.
- Anti-malware sofware. These solutions detect, prevent, and remove malicious software from your device, from viruses to worms to Trojans. It’s best to choose anti-malware software with sophisticated techniques such as behavior-based detection and sandboxing. (You can check out our article on the Best Solutions to Protect Against Malware here).
- Application security. Ensure all software installed on your endpoint devices is protected throughout its lifecycle. The primary goal is to prevent the theft or hijacking of data within the application. Depending on your needs, this may occasionally include application whitelisting.
- Behavioral analytics. A subset of data analytics, behavioral analytics (also known as user and entity behavior analytics) attempts to predict human behavior. It identifies patterns and trends in your end-users and automatically notifies you of any suspicious activity. This is critical in detecting any vulnerabilities.
- Data loss prevention (DLP). Set clear standards to prevent unsafe or inappropriate sharing, transferring, or using sensitive data. All DLP strategies include regular cybersecurity training so all team members learn to protect the personally identifiable information (PII) in their organizations.
- Firewalls. A firewall filters incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. As its name suggests, it is a barrier between a trusted network and an unknown one. The firewall administrator sets the rules for allowing or blocking data packets or network nodes. (It is highly recommended that you read about how to set up your firewall).
- Mobile device security. Mobile device security protects all mobile devices in your IT estate. It involves securing sensitive data and preventing any unauthorized access to the enterprise network.
- Network segmentation. This divides (or segments) your network into smaller pieces to improve performance and security. By controlling the amount of traffic flowing in each segment, you can improve operational efficiency, limit cyberattack damage, and protect vulnerable devices.
- VPN. A virtual private network protects a network connection, especially when using public networks. VPNs encrypt your internet traffic and help disguise your online identity. This significantly reduces the risk of third parties tracking your online activities and stealing data. (We’ve written another guide on the 8 VPN Best Practices to Improve your Security for further guidance.)
3. Application security
Application security involves implementing security features to shield against attackers at the application level. These features include authentication, authorization, encryption, and logging.
Considerations for your application security checklist
- DevSecOps. Also known as the shift-left approach, DevSecOps is an extension of the DevOps model that helps the development team integrate security into all phases of software development across your IT environment.
🥷 NinjaOne has created its own DevOps checklist, listing the 7 best practices for software deployment.
- Secure SDLC Management. The secure software development lifecycle (SDLC) management process covers the product lifecycle from a security point of view. It ensures that all applications are properly developed and maintained, built in a secure environment using best practices, and securely delivered to customers.
- Open-source vulnerabilties. Using open-source tools may expose you to many vulnerabilities despite its advantages. If your organization uses such tools, it’s best to design strategies for regular updates and patching to minimize any risks.
- Automation. Whenever possible, leverage IT automation for simple and time-consuming tasks. Not only does this reduce the risk of human error, but also allows you to optimize your business processes.
- Encryption. Both data at rest and in transit must be encrypted, especially if you manage sensitive data. In today’s age, it is unacceptable for PII to be stored in plain text, as this makes it incredibly easy for hackers to perform man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
- Pentesting. Pentesting is a security exercise that attempts to find and exploit vulnerabilities in your computer system or network. While it is recommended for every business, it is particularly encouraged for larger organizations.
- Authentication. This is a fundamental part of any application security checklist, establishing the identity of users interacting with your application. Authentication includes strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), password storage, and account lockout mechanisms.
4. Data security
Data security protects your IT assets throughout their entire lifecycle. This includes the storage of data, access of data, transportation of data, and proper disposal of data. Common data security solutions include data discovery and classification, data encryption, data backup and recovery, data segmentation, and more.
Considerations for your data security checklist
- Data access. You need to determine where your sensitive data is located and who can access it at any time. Data access strategies include closely monitoring users with admin privileges, changing access permissions as needed (or privileged access management), and auditing any security groups and configuration changes.
- User behavior. Detect who your high-risk users are so you can spot any abnormalities in their behavior. This includes modifications (e.g., strange copying, moving, renaming, creating, or deleting) of data to multiple failed log-ins.
- Security states. It’s important that you regularly audit your security state, such as by looking out for inactive/disabled users, stale or dirty data, empty security groups, or not having a lightweight directory access protocol.
5. User security
Around 60% of CISOs worldwide believe human error is their organization’s biggest cyber vulnerability (Statistica). It’s easy to see why. People are not machines; they can become distracted, easily deceived, and unpredictable. This makes it easier for threat actors to enter and compromise systems. Security actions to protect users include phishing simulations, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and background checks.
Considerations for your user security checklist
- Enforce HTTPS. Though considered “basic” by some, enforcing an HTTPS policy in your organization ensures that data exchanged between devices remains confidential and tamper-proof.
- Limit public database access. While it cannot be avoided entirely, make sure that your team members only allow access from trusted sources. This means rarely using public Wi-Fi when dealing with company information.
- Manage private tokens. Private tokens, such as API keys, need to be securely managed. We recommend regularly rotating tokens, such as through OAuth, to prevent them from being compromised. (You can check out our guide on the 8 Best Practices for Securing APIs here).
- Educate your team. Build a culture of security in your organization, particularly regarding phishing and social engineering. Your team must be regularly trained on these topics because if they succeed, they can render many security measures useless.
Your checklists determine how you will perform your IT audit, but do you know how to execute one properly?
Let’s take a deep dive into IT audits with this how-to guide.
Protecting your assets: Defining the functions
Now that we’ve discussed the asset dimension, let’s move on to the function dimension. In the original Cyber Defense Matrix, Yu classified these functions as either left or right of the “boom”, or happening before or after a cybersecurity event.
It’s best depicted in this image:
Identify
The identify function encompasses the actions necessary to inventory all your assets and understand your current security landscape. This can include performing a vulnerability assessment or analyzing your attack surface. Investing in proper tests and measurements will give you a greater understanding of where gaps are and what may need increased attention.
Protect
Protecting your assets involves hardening, patching, and vulnerability management. It may also include actions taken after recognizing malware, such as isolating a virus to prevent it from infecting other IT assets. Examples of the protect function are applying secure Windows configurations and installing EDR/AV.
Detect
Detection relies on both people and technology, and it is used after a cyberattack has commenced. The detect function recognizes threat actors or cybersecurity events, which can be accomplished through human discovery, active search, or automatic alerts when activity in the IT environment deviates from the norm.
Respond
The response to the event is how you eradicate the cyber threat. How quickly you can respond and the successful removal of the threat will determine the outcome of the event, so it is critical to have a thought-out plan with effective response strategies in place. This function also covers how you assess the damage that was done.
Recover
The final function is to recover. After you’ve been hit by a cyberattack, you’ll have to find a way to pull through to restore and return to your daily business operations. All five functions are very important, but the final function of recovery will show the strength of your IT security strategy as you restore damaged assets and return to normal. Hopefully, after experiencing an attack, you’ll also be able to recognize and record ways you can improve your IT security strategy in the future.
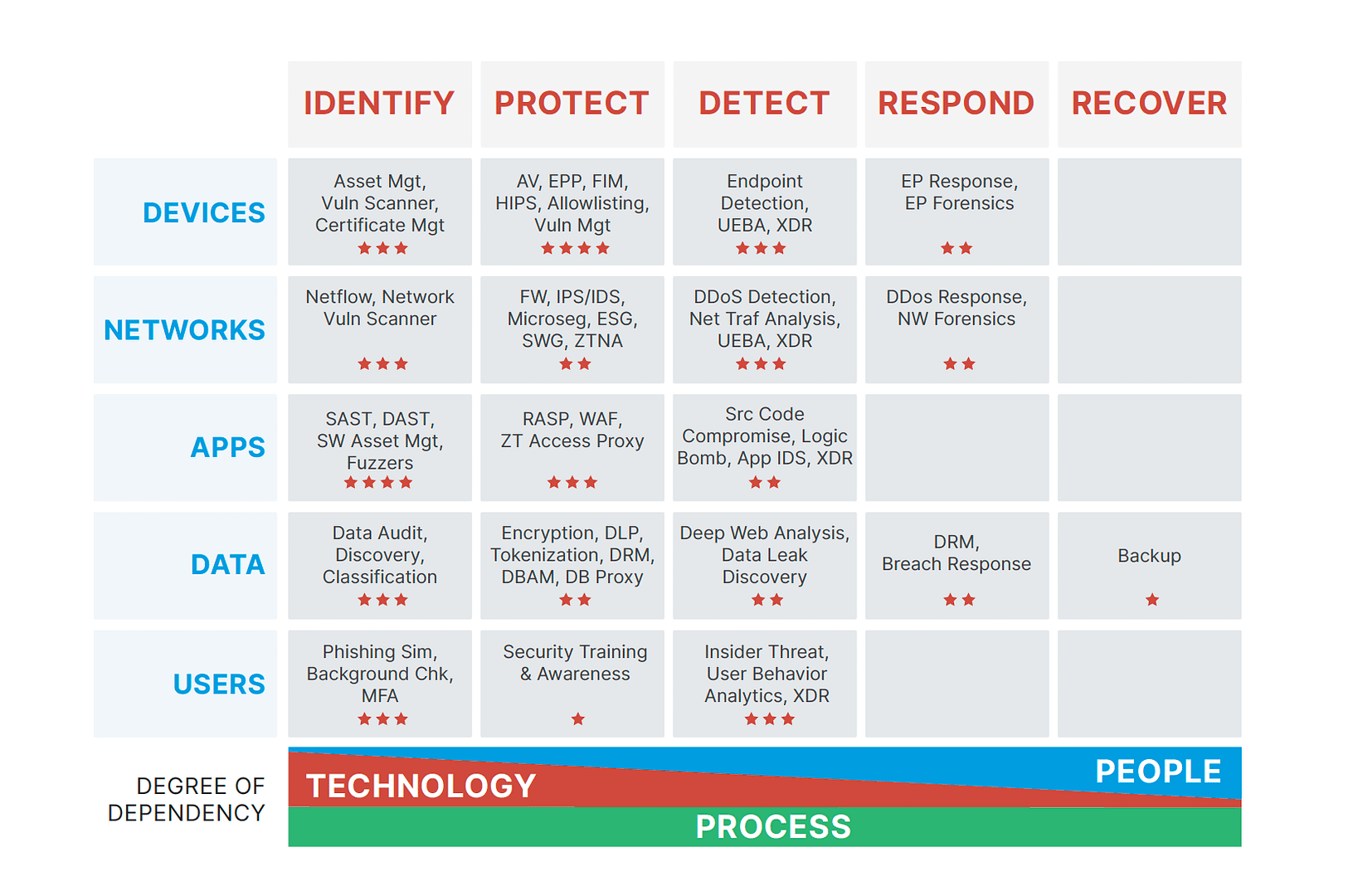
Using the Cyber Defense Matrix, you should now have a checklist that looks something like this:
Remember that every organization is unique, so yours will probably differ from this example.
As you’re conducting your IT security assessment or audit, be sure to also keep these best practices in mind:
Cybersecurity best practices
Define your IT security goals
What specific objectives are you trying to accomplish with your IT security? Begin by outlining the IT aims of the business and what exactly the audit is checking for. Identify what vulnerabilities you are trying to manage or potential gaps or issues you want to mitigate.
Develop security policies
IT security policies spell out the rules and expectations for how individuals in your company access and utilize technology. Develop and review these policies so everyone is on the same page.
Update and enforce security policies
Experts predict businesses will increasingly implement new digital technologies in 2024 to adapt and thrive in the ever-evolving IT landscape. This will lead to worldwide IT spending reaching around $5 trillion by the end of this year (Statistica). To maintain your competitive advantage, you must continually update security policies to meet the evolving technologies, tools, and ways to deal with data.
Backup data
It’s highly encouraged that you be strategic about regularly backing up your data and training team members on managing these backups. Aside from developing your disaster recovery plan, it is a good idea to work with a trusted vendor like NinjaOne that offers backup software and data recovery tools.
Inform all business employees
Anyone with access to any technology within the organization needs to have a basic knowledge of cybersecurity policies in place and understand their role in an IT security audit.
Reference applicable security requirements
Depending on which industry your organization is in, there are certain data protection laws in place. Identify which security framework fits your business and then reference the associated security requirements during the IT security audit.
Account for all assets
Make sure that all your IT assets are inventoried. Knowing how all the assets relate and work together helps in the IT audit, so creating a network diagram is beneficial.
Assign security roles and responsibilities
Outline who is responsible for which cybersecurity responsibilities. This will help you create an escalation matrix, so you know who to contact at certain levels when cybersecurity incidents occur.
🥷 NinjaOne has made the ultimate MSP cybersecurity checklist to prevent the worst scenario from ever happening.
How NinjaOne supports your IT security checklist
NinjaOne is the trusted endpoint management company for 17,000+ clients worldwide. Part of its success lies in its ability to automate the hardest parts of IT, drive radical efficiency from day one, and significantly reduce your IT risk.
Reading this guide may have been overwhelming, but you can rest easy knowing that NinjaOne can check most boxes in your IT security checklist—whether you’re managing 50 or 50,000 endpoints.
Specifically, NinjaOne provides the visibility, control, and tools you need to deploy foundational security strategies across your entire IT infrastructure with its enterprise IT security tool.
If you’re ready, request a free quote, sign up for a 14-day free trial, or watch a demo.