There are many moving parts to a zero trust strategy, and network segmentation cybersecurity is an important piece of the puzzle. Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to minimize the potential damage caused by unauthorized access or attacks.
In this article, we will explore the role of network segmentation in security, the key principles behind it, and ten network segmentation best practices to implement it effectively.
NinjaOne RMM lets you manage any device on any network from wherever you are.
What is network segmentation?
Network segmentation, also known as network partitioning or network isolation, is the practice of splitting—or segmenting—an internal network into multiple smaller parts to improve performance and security. Depending on how your organization is designed, your IT team can leverage its network segmentation policy to adapt to different security levels. This prevents a single point of failure to compromise the entire network.
This is particularly useful for modern hybrid workforces, where organizations and departments are heavily interconnected. Any malicious traffic will not immediately disrupt your entire IT environment but will be isolated or contained within a segment. This gives your security team enough time to locate the breach and perform necessary remediation.
The role of network segmentation in security
Network segmentation plays a vital role in enhancing security by limiting the lateral movement of bad actors within your network. Splitting a network into smaller, secure subnetworks helps contain breaches or attacks within one area, stopping them from spreading throughout the whole network.
Think about it like a mansion that has dozens of rooms, which you divide into sections (subnetworks), with locks on each section’s doors (implementing security controls). If an intruder enters one section, they’re confined to that area alone. This prevents them from accessing the entire mansion, much like how segmenting a network restricts a breach to just one subnetwork, protecting the rest of your network.
Network segmentation cybersecurity is generally divided into two main types: physical and logical segmentation.
- Physical segmentation entails using tangible hardware, such as switches and routers, to separate networks. It’s similar to constructing physical barriers within a building.
- Logical segmentation, on the other hand, involves dividing networks through software tools or configurations, such as virtual local area networks (VLANs). This method offers more flexibility and can be customized to meet your specific needs.
Key principles of network segmentation
To effectively implement network segmentation best practices, you need to understand the key principles that underpin its effectiveness.
- Principle of least privilege: Each segment should only have access to the resources and services necessary for its intended purpose, which limits the potential attack surface.
- Secure boundaries: Boundaries between segments should be well-defined and protected to prevent unauthorized access. Strong access controls, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, should be implemented to monitor and control traffic flow between segments.
- Monitoring and logging: Comprehensive monitoring and logging mechanisms should be in place to detect and track any suspicious activity within each segment. This allows you to identify potential security incidents promptly and take appropriate action to mitigate them.
10 network segmentation best practices
Implementing a robust network segmentation strategy requires careful planning and execution. Here are ten best practices and some useful technologies to consider when completing your network segmentation design.
1. Identify critical assets
Begin by identifying the critical assets within your organization. These could include sensitive data, intellectual property or systems that are crucial for your operations. Understanding the value and importance of these assets will help you determine the level of segmentation required to protect them and ensure that the most sensitive and crucial areas are secured first. This network segmentation strategy approach safeguards your key assets and optimizes resource allocation to protect high-priority areas.
2. Conduct a risk assessment
When searching for network segmentation best practices, one action that is always emphasized is regular risk assessments. A thorough risk assessment is crucial for identifying potential security vulnerabilities and external threats to the network. This step is instrumental in understanding your security landscape, identifying gaps in your defenses and evaluating how much time and effort you will require to improve your security posture. It will also help you concentrate your efforts on the areas where you are weakest, without overlooking less obvious points of vulnerability.
3. Define network segmentation policy
Creating a clear, concise network segmentation policy and guidelines is vital for the success of your network segmentation design. These policies should:
- Outline the criteria for segmenting the network, whether by department, function or data sensitivity.
- Align with your overall security objectives, ensuring a unified and strategic approach to network security.
- Facilitate a structured implementation that meets specific goals and objectives at specific points in time.
4. Use VLANs and subnets
A key aspect of your network segmentation design is utilizing VLANs and subnets to separate network parts logically. VLANs can prioritize certain types of traffic over others, ensuring optimal performance for critical applications. You can assign specific VLANs or subnets to different segments to control access and communication between groups. This logical separation is crucial for minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and ensuring efficient network operation.
5. Implement Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are essential for managing and controlling traffic flow between network segments. They allow your administrators to specify rules that govern the types of traffic allowed or denied, ensuring that only authorized communications occur between segments.
Ensure that your network segmentation policy includes regular review and update of ACLs to keep them effective and ensure you adapt to any network or security requirements changes. This continuous adjustment is key to preserving a secure and functional network environment.
6. Deploy firewalls
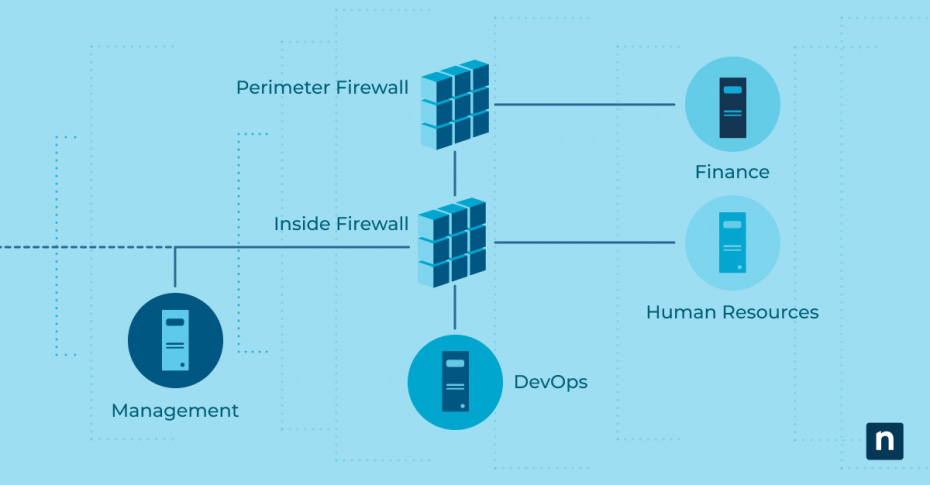
No list of network segmentation best practices is complete without considering firewalls. Firewalls act as gatekeepers to granularly monitor and control traffic between network segments, uncovering suspicious patterns and offering an additional layer of security. Implementing both perimeter and internal firewalls with detailed security policies and protocol or application-based segmentation creates a multi-layered security approach and strengthens your overall network segmentation strategy
Firewalls can also create demilitarized zones, isolating public-facing servers from the internal network. This significantly enhances your defense mechanisms against both external and internal threats.
7. Consider micro-segmentation
Micro-segmentation is a cybersecurity strategy that goes beyond traditional network segmentation design to create highly specific, secure zones within data centers and cloud environments. One of the lesser-known network segmentation best practices, micro-segmentation involves by breaking down network segments into smaller, more granular sub-segments—or even segmenting by individual workloads—which gives you more precise control over traffic and more tailored security policies.
It also allows you to define security policies based on the specific needs of each workload, regardless of its location in the cloud or on-premises. This flexibility is crucial for hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
8. Regularly test and update
Network segmentation is not a one-time effort but a continuous process that demands regular monitoring, testing and updating to remain effective. Conduct periodic penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify weaknesses or gaps in your segmentation strategy and adjust accordingly.
In addition, keep your segmentation policies and controls current so you can effectively counter evolving threats and accommodate changes in your network infrastructure. This ongoing diligence ensures the long-term effectiveness and resilience of your network segmentation strategy.
9. Educate your team
An excellent network segmentation policy is not just about technology—it also requires a well-informed team. All team members, even those not in IT, play a crucial role in maintaining the security of segmented networks. It’s a good idea to provide cybersecurity awareness training, such as the “Like a Ninja” community streams, that talk about various strategies to reduce vulnerabilities.
IT staff, in particular, need specialized training to design, implement, and manage network segmentation policies effectively. Regular workshops, certifications, and simulation exercises can help your team stay updated on best practices and emerging threats.
10. Plan for scalability
An excellent network segmentation plan should be future-proof to accommodate future growth and complexity. This means regularly assessing your network architecture. After each review, determine where segmentation may need to be expanded or refined to keep up with evolving operational needs. It’s also a good idea to design segmentation policies that can easily scale for new departments, users, or applications without requiring a complete overhaul of your network.
In addition, it’s a good idea to leverage automation to streamline policy enforcement and reduce the risk of human error as your network scales. Automated tools can adjust network segmentation rules based on real-time data and ensure your network remains secure and efficient as it grows.
9 benefits of implementing network segmentation best practices
Network segmentation stands as a cornerstone strategy in modern cybersecurity, offering a multi-faceted approach to protecting your organization’s digital assets. By implementing network segmentation best practices, you can enjoy several advantages in security, compliance and operational efficiency.
In IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024, the global average cost of a data breach was $4.48M—a 10% increase from 2023 and the highest total ever. Experts agree that this figure will only increase in the coming years, especially as threat actors become more sophisticated and current cybercrime statistics show a growing trend in more evolved cyberattacks.
A robust network segmentation strategy is essential for organizations looking to secure their complex networks. This is because the practice can:
- Reduced risk: A strong network segmentation policy significantly reduces the risk of lateral movement by containing threats within specific segments. This containment prevents attackers from moving freely across your network, minimizing the potential damage of a security incident.
- Provide granular access control: Network segmentation allows for more precise access controls, ensuring users can only access what they’re authorized to use.
- Mitigate advanced threats: Micro-segmentation further divides network zones, which provides more robust protection against sophisticated threats like ransomware.
- Improve compliance: Network segmentation best practices help your organization comply with various regulatory standards by isolating sensitive data and systems. It simplifies demonstrating compliance and reduces the scope of audits and assessments for regulations like GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA, among others..
- Optimize auditing process: By defining clear network boundaries and segmenting sensitive environments, organizations can streamline the scope and effort of compliance assessments.
- Improve operational resilience: In the event of a security incident, network segmentation allows you to isolate and contain the impact, minimizing downtime and disruption to critical operations.
- Maintain business continuity: Following network segmentation best practices ensure unaffected areas remain operational during an incident.
- Recover faster: Isolated segments enable quicker identification and resolution, which results in a lower mean time to recover (MTTR)
- Reduce congestion: A well-designed network segmentation design can optimize traffic flow, reduce bottlenecks, and improve overall system performance.
💻 Increase automation and efficiencies with the #1 RMM, according to G2.
How NinjaOne fits in with your network segmentation strategy
Network segmentation best practices are a critical security measure that your organization must implement to protect your sensitive information. By following the key principles and best practices outlined in this article, you can elevate your security posture and minimize the potential impact of security incidents.
NinjaOne is an endpoint management company trusted by 20,000+ customers worldwide. It’s all-in-one platform automates the hardest parts of IT so IT enterprises of all sizes can experience radical efficiency from day one. NinjaOne RMM is proven to increase technician efficiency by 95% with out-of-the-box automation that supports complex, multi-step workflows. This, along with its intuitive UI and numerous integrations, has helped the platform be consistently rated #1 by G2 for years.
NinjaOne’s IT management software has no forced commitments and no hidden fees. If you’re ready, request a free quote, sign up for a 14-day free trial, or watch a demo.