Patching vulnerable software and systems is more important and challenging to keep up with than ever. Here’s how IT pros can make their patch management process more efficient, eliminate disruption, and keep their networks secure.
What is patch management?
Automatically identify and remediate vulnerabilities across your entire IT portfolio at speed and scale from a single pane of glass – no infrastructure required.
While Windows devices still dominate the business market, Mac and Linux endpoints are becoming more prevalent. Modern patch management requires a tool to secure all three operating systems effectively.
Download our guide to learn how to evaluate your organization’s patching readiness and how to assess potential solutions.
Why is the patch management process important?
Patching keeps systems and applications running smoothly and is also one of the core activities involved in keeping today’s organizations secure. Leaving machines unpatched makes them vulnerable to cyber attacks, and the risk is anything but theoretical. In fact, according to the Ponemon Institute, the majority of data breaches (57%) can be directly attributed to attackers exploiting a known vulnerability that hadn’t been patched.
A quick scan of security-related headlines offers plenty of examples, from Equifax (culprit: a two-month-old unpatched Apache Struts vulnerability) to SingHealth (data for 1.5 million patients exposed thanks to an outdated version of Outlook).
All resulted in highly publicized security incidents and data breaches that could have otherwise been avoided with a more rigorous and efficient patch management process..
The sudden scramble to get employees working remotely during the COVID crisis has compounded the issue, with attackers routinely seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in popular Virtual Private Network (VPN) solutions, including:
- Citrix (CVE-2019-19781)
- Palo Alto (CVE-2020-2021)
- Pulse Secure (CVE-2019-11510)
- SonicWall (CVE-2020-5135).
The challenge for small and medium-sized businesses
If some of the largest, most well-funded organizations in the world are having difficulties with patch management, what chance do small and medium-sized businesses with limited IT support have?
More than 18,000 CVEs were published in 2020.
Source: InfoSecurity Magazine
Some of the biggest difficulties with patching center around the fact that the process can be time-consuming, complicated, and disruptive to end users. As a result, it’s easy to put patching off or simply have important updates get lost in the shuffle. And with more than 18,000 CVEs published in 2020, it’s no surprise many organizations have difficulty keeping up.
The average time to patch is 102 days.
Source: Ponemon
Unfortunately, the risk unpatched systems pose is increasing. Once a vulnerability has been disclosed and a patch has been released it’s a race for organizations to apply the patch before attackers begin actively exploiting it. That window of time is shrinking dramatically, with numerous recent examples where attackers were able to launch attacks abusing new vulnerabilities prior to or just days following their disclosure.
Once working exploits have been developed, they quickly gain widespread adoption. Scanning tools like Shodan, nmap, and Masscan then make it trivial for attackers to identify vulnerable systems and launch targeted campaigns.
For many small businesses, the solution to staying on top of patching cycles is to outsource the burden to managed services providers (MSPs). But how are the most effective MSPs tackling the problem?
Learn how the Syscomm Group was able to leverage NinjaOne to get the most out of their security monitoring.
“We use Ninja to automate patching across our end-user devices and servers. We save a ton of time on patching now as we no longer have any manual steps in our patching workflow.”
Martin Wells, CEO of Syscomm Group
10 key steps in a patch management process
Below is a 10-step patch management process template highlighting the fundamental considerations that need to go into any patch management plan. Before diving into this workflow you’ll want to make sure you’ve established clear roles and responsibilities for each step, and that all key stakeholders are fully on board.
Step 1: Discovery
First, you need to ensure you have a comprehensive network inventory. This includes understanding the types of devices, operating systems, OS versions, and third-party applications at the most basic level. Many breaches originate because IT has neglected or forgotten systems. MSPs should utilize tools that enable them to scan their clients’ environments and get comprehensive snapshots of everything on the network.
Step 2: Categorization
Segment-managed systems and/or users according to risk and priority. Examples could be by machine type (server, laptop, etc.), OS, OS version, user role, etc. This will allow you to create more granular patching policies instead of taking a one-policy-fits-all approach.
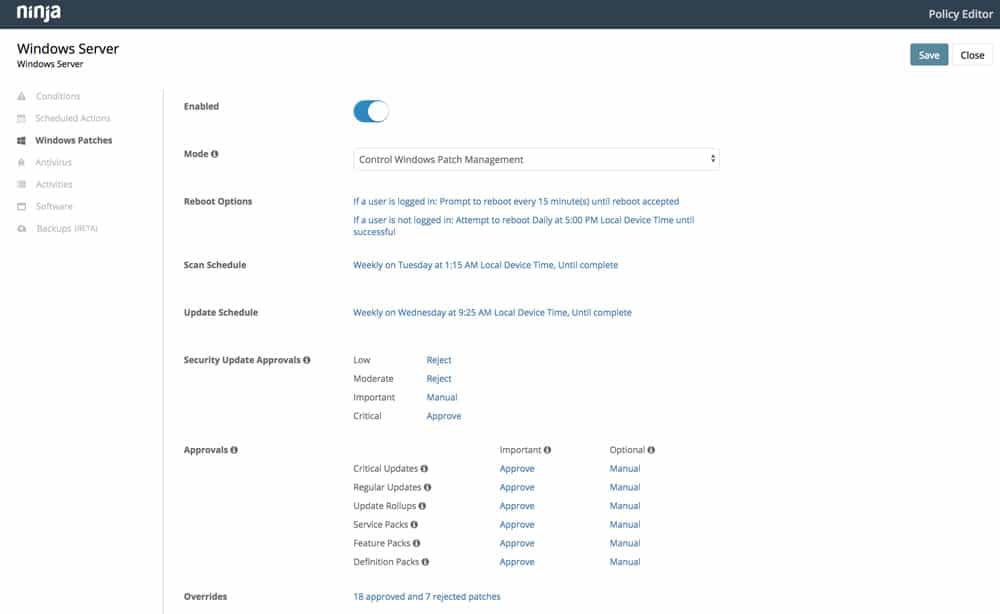
Step 3: Patch management policy creation
Create patching criteria by establishing what will be patched and when, under what conditions. For example, you may want to ensure some systems/users are patched more frequently and automatically than others (the patching schedule for laptop end users may be weekly while patching for servers may be less frequent and more manual). You may also want to treat different types of patches differently, with some having a quicker or more extensive rollout process (think browser updates vs. OS updates; critical vs. non-critical updates, for example). Finally, you’ll want to identify maintenance windows to avoid disruption (take into account time zones for “follow the sun” patching, etc.) and create exceptions.
Step 4: Monitor for new patches and vulnerabilities
Understand vendor patch release schedules and models, and identify reliable sources for timely vulnerability disclosures. Create a process for evaluating emergency patches.
Step 5: Patch testing
Create a testing environment or at the very least a testing segment to avoid being caught off guard by unintended issues. That should include creating backups for easy rollback if necessary. Validate successful deployment and monitor for incompatibility or performance issues.
Step 6: Configuration management
Document any changes about to be made via patching. This will come in handy should you run into any issues with patch deployment beyond the initial test segment or environment.
Step 7: Patch rollout
Follow the established patch management policies you created in step 3.
Step 8: Patch auditing
Conduct a patch management audit to identify any failed or pending patches, and be sure to continue monitoring for any unexpected incompatibility or performance issues. Tapping specific end users who can help by being additional eyes and ears is also a good idea.
Step 9: Reporting
Produce a patch compliance report you can share with your clients to gain visibility into your work.
Step 10: Review, improve, and repeat
Establish a cadence for repeating and optimizing steps 1-9. This should include phasing out or isolating any outdated or unsupported machines, reviewing your policies, and revisiting exceptions to verify whether they still apply or are necessary.
What are the best practices for Patch Management?
As the demand for effective patch management continues to become more integral, MSPs need to improve on their own process and offerings or risk falling behind. Here are three keys to MSPs providing smarter, more efficient, and more effective patch management services in 2022.
1) Automate patch updates
Patching is a game that’s extremely easy to fall behind in, especially if you’re still relying on identifying, evaluating, and deploying patches manually. Cloud-based, automated patch management software allows MSPs to schedule regular update scans, and ensure patches are applied under specific conditions or automatically.
How NinjaOne can help:
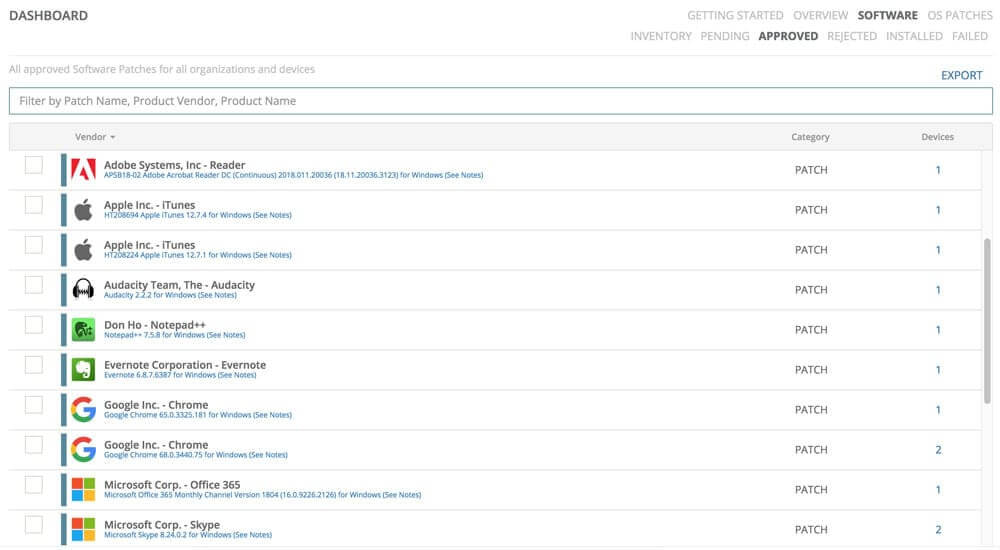
- Automate patching for Windows and third-party software from over 120 vendors.
- Easily configure patch scanning and update schedules for specific segments of devices or users. Get granular control or set it and forget it.
- Less time combining through new update releases and vulnerability disclosures, more time growing your business.
2) Mitigate patch deployment validation with audit reports
Despite patching automation becoming increasingly popular, MSPs unfortunately can’t always assume automated patching solutions are working as promised. That means time-consuming, manual validation. Developing scripts or processes to ease that burden (or, better yet, utilizing solutions that don’t require double-checking) is a worthwhile investment.
How NinjaOne can help:
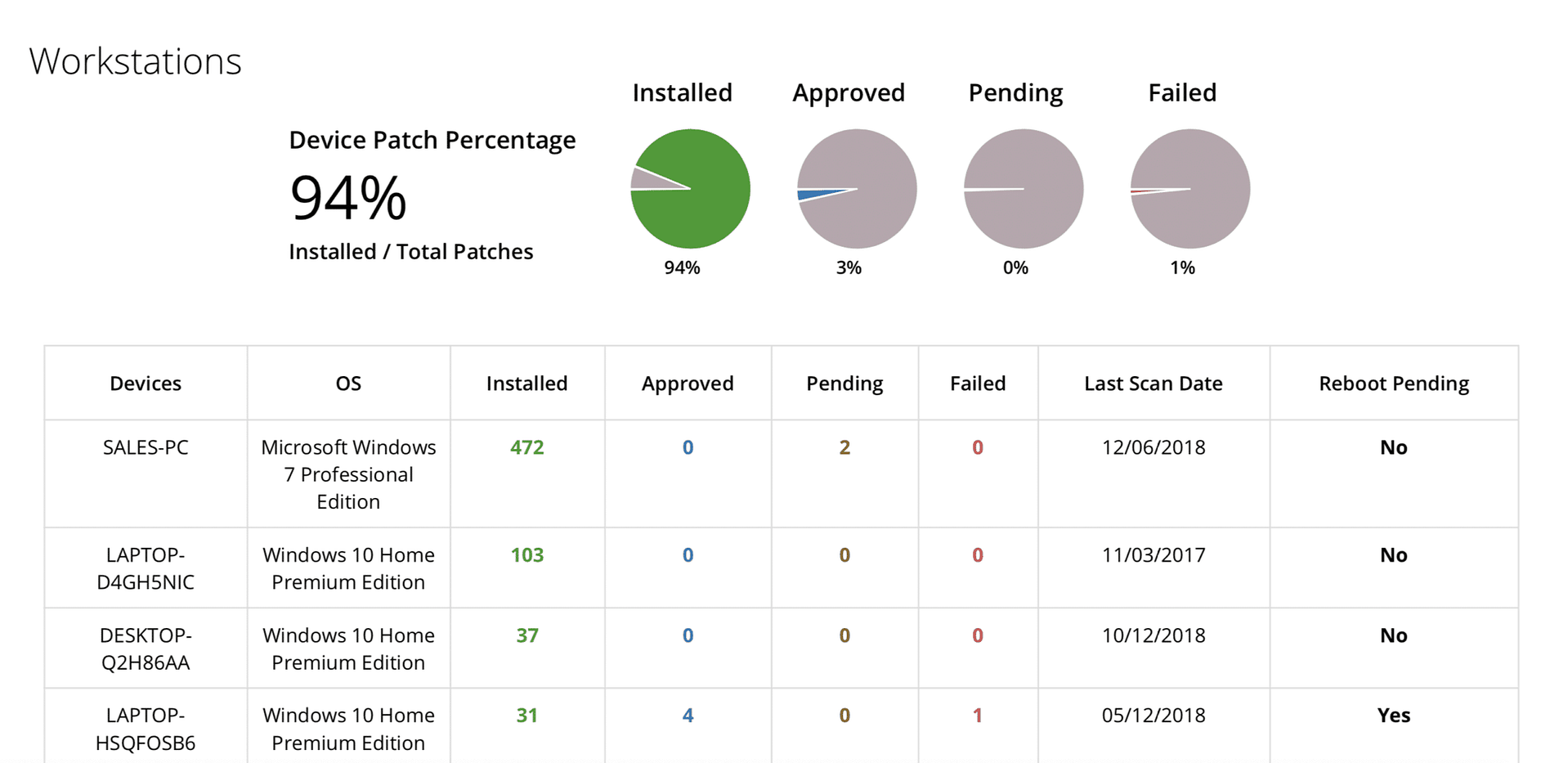
- Gain access to detailed patch audit reporting.
- Eliminate the guesswork by ensuring you have access to reliable real-time information.
3) Streamline reporting
Everything you do as an MSP should be communicated as value-add to your clients. Patch management should be no exception, but delivering patch management audit reports should be as automatic as possible. After all, the more time reporting takes, the less time you have for providing additional services and growing your business.
Step-by-step instructions for implementing your patch management process
The ultimate goal of patch management is to ensure that all software solutions in your managed fleet are updated to keep your IT network healthy. Generally, the patch management process includes these steps.
-
Determine baseline data
You don’t know what you don’t know—and the same applies to your software patch management process. The first step is determining your baseline data by developing an inventory of all software programs in your organization. This gives you a better understanding of what devices must be patched, which fixes have been implemented, and which may be missing. This, in turn, allows you to build a more comprehensive patch management procedure.
-
Establish priorities based on risk and criticality
After reviewing which endpoints need to be patched and identifying their software applications, you must first set a hierarchy on which patches need to be implemented. Establish priorities based on their level of importance and potential attack path. Designing your process like this guarantees that high-risk vulnerabilities are immediately resolved before they turn into bigger problems.
-
Create a patch management policy
This policy must clearly state the processes that must be followed and reported on per device and software. It should also determine how and when security patches should be deployed and any other rules needed for patching and upgrades.
Arguably, this may be the lengthiest step in your overall strategy. However, your organization’s patch management policy should be easy to understand and implement. It should plainly describe your techniques, guidelines, roles and responsibilities, and a thorough documentation process before and after patching.
-
Test patches
Ensure that patches are assessed and tested before they are implemented and deployed to your entire organization. This testing stage helps you evaluate the patches in a controlled environment and personally observe any potential incompatibilities or negative effects of your server patching. You may conduct steps 3 to 4 as needed.
-
Backup
Even when you feel that your policy is “perfect”, it’s highly recommended that you completely back up your key systems and data before applying any fixes. This serves as a safety net in case problems occur during security patching. You may also want to consider a data recovery tool to restore your systems in the event of a disaster easily.
NinjaOne’s data recovery software offers comprehensive backup and swift data recovery.
-
Monitor patch updates and fix issues
Given the ever-evolving business and IT landscape, it’s crucial that you continuously monitor your patch management process. Verify if your patches were successfully installed, check if you comply with various regulatory standards, such as the GDPR and PCI DSS, and keep yourself updated on any new patches that need applying.
How NinjaOne can help:
- Generate patch compliance reports that highlight the number of patches you’ve applied.
- Give your hard work more visibility with your clients.
- Ensure your tools are up to the task.