This tutorial provides instructions to see if a process is 32-bit or 64-bit in Windows 10 and Windows 11. It shows you step-by-step how to use the task manager or PowerShell to check process architecture, and explains the significance of whether a process is 32-bit or 64-bit.
The difference between 32-bit and 64-bit processes on Windows
The number of ‘bits’ determines how much data a process can handle: a 32-bit process can handle 32 bits of data at once, while a 64-bit process can handle 64 bits of data. This affects performance and also goes on to affect how much memory (RAM) a process can access. 32-bit processes can address up to 4GB of RAM (2^32 memory addresses), while 64-bit processes can access up to 16 exabytes (2^64 memory addresses).
The ability to work with more data and access more memory makes 64-bit applications much faster for resource-intensive tasks.
32-bit vs. 64-bit processes
A process can only run on an operating system and with a CPU that is designed to handle the same number or more bits.
From the mid-90s and the release of Windows NT, 32-bit became the most common software platform (though 32-bit processes had been popular since the mid-1980s Intel 386). In the late 2000s, 64-bit processors became more widely available (and affordable), and by the 2010s, most operating systems and applications started to prioritize 64-bit releases.
What this means for Windows users
Most operating systems, including Windows, allow you to run 32-bit software on 64-bit systems. The reverse is not possible, however — you cannot run 64-bit Windows software on 32-bit Windows operating systems. Generally, if you are running a 64-bit version of Windows 10 or Windows 11, you should run 64-bit apps if they are available as they will perform faster.
How to tell if a process is 32-bit or 64-bit in Windows 10/Windows 11 with the Task Manager
These instructions will tell you if a process is 32-bit or 64-bit in Windows 10 and Windows 11 using the Task Manager.
Note that these instructions are only for 64-bit versions of Windows, since if you’re running a 32-bit operating system, any running processes can only be 32-bit.
- Right-click on the Start button
- Click Task Manager
- On Windows 10, you may need to click More Details to view the full list of running processes
- If a process has a (32 bit) label next to it, it is a 32-bit process
- If there is no label, it is a 64-bit process

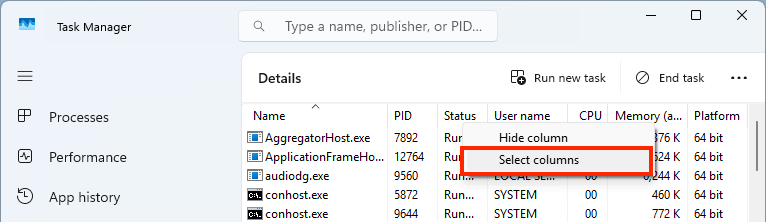
You can also determine whether a Windows process is 32-bit or 64-bit using the details tab in the Task Manager:
- Click on the Details tab in the Task Manager
- Right-click on the column headings and press Select columns
- Scroll through the list of columns and check Platform
- Click OK to confirm the change
- You will now be able to determine whether an app is 32-bit or 64-bit using the Platform column in the Task Manager Details tab
Ensuring the best performance of all devices in enterprise deployments
Running 32-bit software in 64-bit environments is often necessary to support legacy software but is not an optimal use of resources if a 64-bit version of the same software is available.
It is important to monitor the performance of Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices in enterprise environments to ensure productivity is not impacted by slow devices and unresponsive software. Poor device performance and unexpected battery drain can also be indicators of malware that can be detrimental to your IT infrastructure, data, and business continuity.
NinjaOne provides a comprehensive, end-to-end Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution that allows you to monitor the performance of Windows, Apple, and Android devices. This helps ensure that you are notified of any anomalous activity so you can quickly identify and remediate device performance and cybersecurity issues.