Secure remote access is now a necessity for organizations, especially since the hybrid work model is expected to grow from 42% in 2021 to 81% in 2024. To secure remote access and provide support for hybrid or fully remote teams, businesses rely on remote access protocols, such as Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). With this post, you can dive deeper into various aspects of RDP, such as pros/cons and use cases, and acquire a better understanding of this essential protocol.
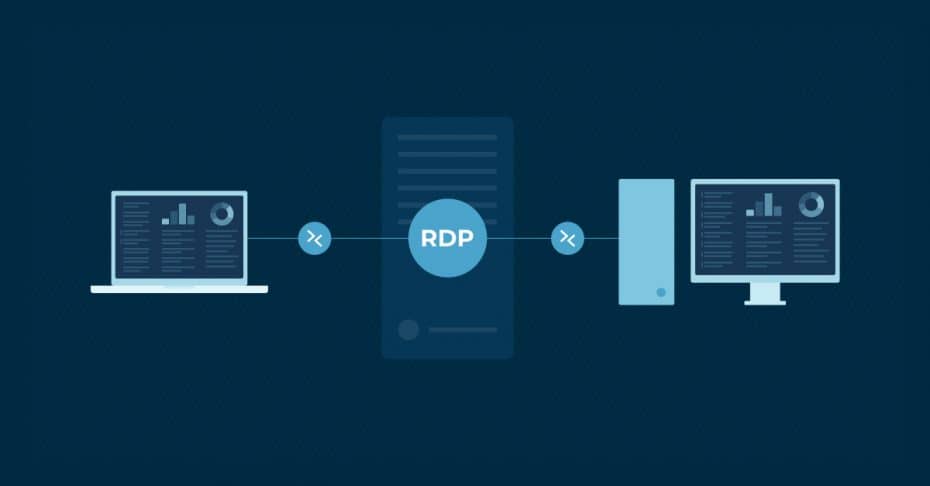
Remote desktop protocol (RDP) is Microsoft’s protocol or set of technical standards for remotely accessing a desktop. It allows two remote devices to exchange information safely over a secure and encrypted communications channel through an RDP server. IT departments use RDP to ensure that they can support and view an entire remote IT infrastructure in a secure manner.
Origins of RDP
Remote Desktop Protocol has been around for a while; to be specific, RDP has been around since 1998. Even though RDP was created over a couple of decades ago, it’s still “an extremely popular protocol for remote access to Windows machines. In fact, there are more than 4.5 million RDP servers exposed to the internet alone, and many more that are accessible from within internal networks,” CyberArk writes. While another protocol might replace RDP in the future, it’s clear that the IT community will continue to use RDP for a while.
How does RDP work?
RDP allows IT professionals to access an endpoint remotely by sending data between two devices, allowing them to communicate over network port 3389. To ensure that all information sent between the devices remains secure, RDP encrypts all transmitted data. This data includes keystrokes, mouse movements, desktop displays, and other essential information. With RDP, a technician will have a complete view of a user’s desktop on their own device and will be able to control or manage the device as well.
Cloudflare clarifies the concept of RDP with this example, “Think of a remote-controlled drone or toy car. The user presses buttons and steers the drone or car from afar, and their commands are transmitted to the vehicle. Using RDP is somewhat like that: the user’s mouse movements and keystrokes are transmitted to their desktop computer remotely, but over the Internet instead of over radio waves. The user’s desktop is displayed on the computer they are connecting from, just as if they were sitting in front of it.”
Eliminate the risks of RDP cons by leveraging NinjaOne Remote Access.
Remote desktop protocol (RDP) use cases
TechTarget explains that there are currently three main use cases for RDP, which are:
Remote access
Remote work has continued to rise ever since the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020, and many companies are choosing to adopt a remote work model permanently. Remote workers can rely on RDP to access a home or office PC while working from different locations or traveling.
Remote support
A popular use case for RDP is remote support. Using RDP, a tech support team can access a desktop to troubleshoot and solve issues. It’s a fast, easy, and efficient way for help desk teams to see and access users’ devices. A remote support software can help streamline troubleshooting and improve your team’s efficiency.
Remote administration
With RDP, technicians can remotely configure devices. With certain RMM tools, such as NinjaOne, you can configure RDP remotely on a device before you access and use it. If you’re looking to streamline your remote management process, a remote administration software can help you manage devices more efficiently and securely across your network.
Pros and cons of remote desktop protocol
All technical solutions have their own pros/cons, and RDP is no exception. Some pros and cons of RDP include:
Remote desktop protocol pros
-
Effective and well-known
One of the main reasons IT teams use RDP is because it works. No one wants to spend time trying to use a tool that’s ineffective or doesn’t perform properly. Additionally, RDP has been around for a while, so it’s easy to find remote access tools that use it and personnel who are familiar with it.
-
Safe and secure connection
From ransomware to spyware, there are all kinds of cybersecurity threats that businesses defend against on a daily basis. When using RDP, MSPs and internal IT members can rest easy knowing that any transmitted data is encrypted and secure.
-
Enables remote work & support
RDP has come in handy these past couple of years, especially as companies transition from on-premise to remote or hybrid workforces. Using RDP, organizations can enable and support their employees regardless of their physical locations.
Remote desktop protocol cons
-
Single monitor support only
Unfortunately, RDP by itself only offers single monitor support and doesn’t allow users to switch between screens. Because of this, providing support for multiple monitors can turn into a hassle.
-
Restricted functionality
A recent RDP overview compares RDP to a VPS, reporting that RDP provides “Less functionality – when compared with a VPS, the potential outcomes of what could be refined with assistance are very restricted. The absence of administrator access basically adds to the usefulness limitations.”
-
No administrative privileges
As aforementioned, RDP by itself does not provide administrative privileges. However, there are tools you can use along with the protocol to gain administrative access.
How to use remote desktop protocol
It’s worth noting that you can’t enable Remote Desktop in all Windows versions. In addition, Windows devices with a Remote Desktop option typically only support a single RDP connection.
That said, using these steps, you can generally enable remote desktop on Windows.
For Windows 10 pro and later systems.
- Click on the Start button, go to settings, click System Settings, and select the Remote Desktop option. Take note of the PC name so you can use it later during the Remote Desktop Connection.
- If possible, enable Network Level Authentication in Advanced Settings to ensure that only authorized users in your organization can connect to the RDP server.
Connect to the remote desktop
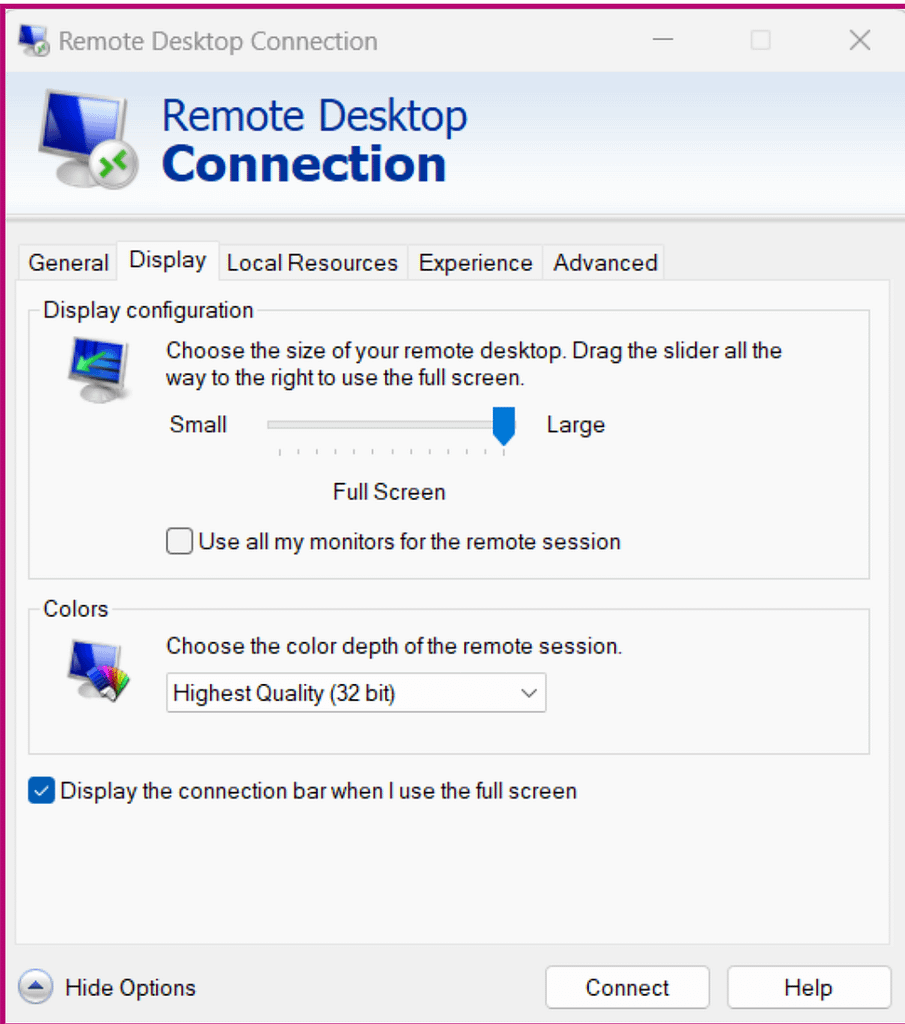
- Type “remote desktop connection” in the search bar and choose Remote Desktop Connection. You should see a screen like this:
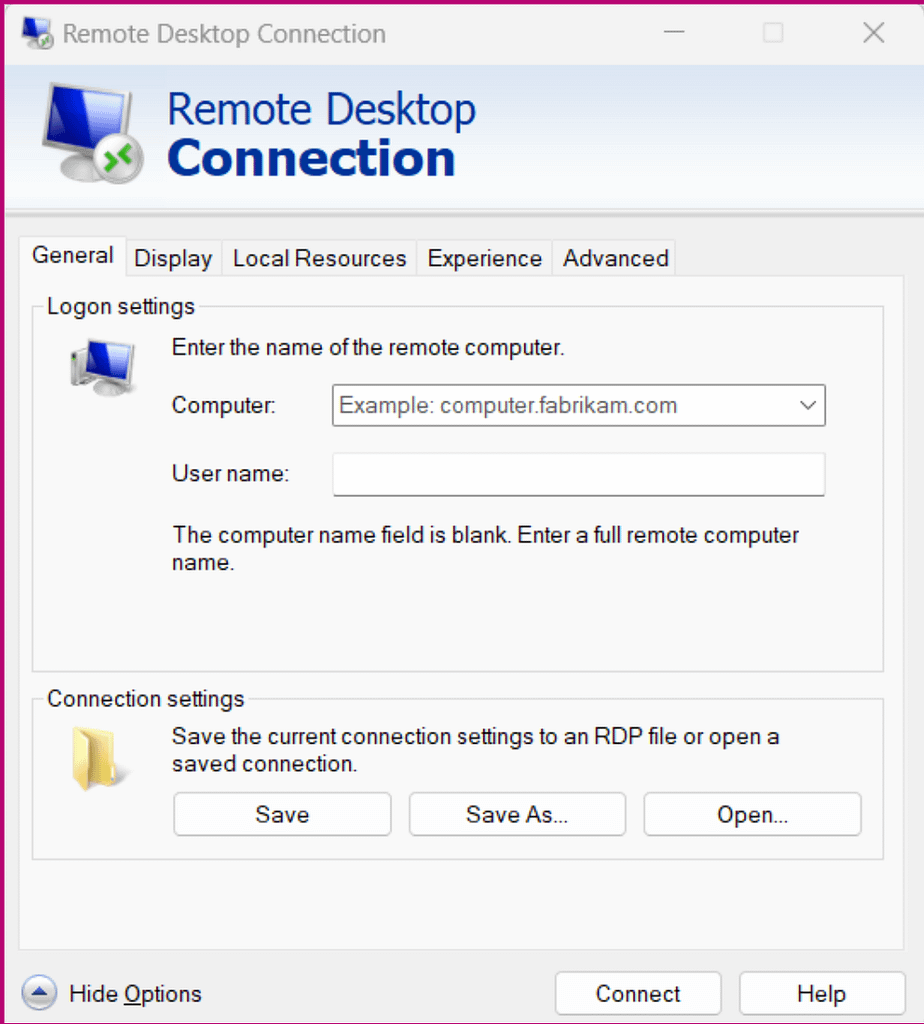
- In the Computer section, type the PC’s name or the computer’s IP address you want to connect to.
- You can change the connection settings from the adjacent tabs, including the display, local connection, and connection quality. Adjust these settings as needed.
- Once done, click Connect.
- Occasionally, you will be prompted with a warning message stating that the computer’s identity hasn’t been verified. You can discard this message and continue to connect. This enables your remote connection.
Secure your remote access using RDP with NinjaOne
With NinjaOne remote access, you can customize your RDP experience to use single or multi-monitor viewing, automatically provision endpoints for RDP access, set up credential exchange integrations for administrative privileges, and much more. By using NinjaOne as your remote access tool, you are able to eliminate various RDP cons, such as single monitor support and restricted functionality, so that you only gain RDP’s benefits. Sign up for your free trial of NinjaOne to get started today.
Reduce security risks associated with direct RDP connections by depending on NinjaOne Remote Access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the difference between RDP and RDS?
It’s easy to confuse the RDP definition with remote desktop services (RDS). However, the easiest way to differentiate the two is to look at the scope of their functionalities. RDP is a protocol that allows you to connect to a remote desktop, whereas RDS is a suite of tools that enables remote access to desktops and applications.
What is the RDP protocol connection?
Essentially, we can describe the RDP meaning as a multi-channel protocol that allows separate channels to communicate and share data over an RDP server. This data delivery is done in real-time to multiple parties.
Is Windows RDP secure?
Windows RDP can be secure when properly configured. By default, a remote desktop session operates through an encrypted channel. However, malware infiltration and brute force attacks may exploit vulnerabilities within a session. You can minimize this risk by working with a vendor like NinjaOne that offers a robust endpoint monitoring and management solution.