Svchost.exe, also known as Service Host, is a system process inherent to the Windows operating system that serves a pivotal role in hosting and managing one or more Windows services.
This process is instrumental in ensuring that various system services run smoothly and efficiently, segregating them into distinct groups to prevent service failures from affecting the entire system.
For both everyday users and IT professionals, understanding the role of svchost.exe is crucial. This guide is dedicated to providing a thorough exploration of svchost.exe, elucidating its purpose within the Windows operating system, and addressing prevalent concerns regarding its security.
It aims to enlighten readers on the intricacies of what is svchost.exe and its nature, detailing its functions and guiding them in discerning whether it is secure or potentially malicious.
You may view this brief video on ‘What Is Svchost.exe and Is It Safe?‘.
Optimize critical processes like svchost.exe with NinjaOne Endpoint Management solutions.
What is svchost.exe?
Svchost.exe is a system process designed to host and manage DLL-based services. It enables multiple instances of itself to run simultaneously, each hosting a different group of services, thus optimizing the use of system resources and ensuring that services are organized based on their categories and security requirements.
In Windows operating systems, svchost.exe is essential for the smooth operation of the system by managing background services that are critical for both system performance and functionality. These services include networking, user interfaces, file management, and more.
Why there are multiple instances of svchost.exe running
- Efficiency in resource usage: Each instance of svchost.exe can run a set of services independently of others, which means if one instance fails, it doesn’t impact the services in another instance.
- Enhanced security: Separate instances allow for different security settings depending on the sensitivity of the services being run, thereby isolating more secure services from less secure ones. In addition, malware has a harder time compromising multiple system components at once, reducing the potential for widespread damage.
- Easier troubleshooting: With fewer services grouped together, diagnosing high resource usage or faulty behavior becomes simpler. Issues can now be traced more efficiently to a specific service.
- Scalability: Multiple instances allow Windows to scale the services horizontally as needed without overloading a single service host.
Historical context and evolution of svhost.exe
Svhost.exe was introduced in Windows 2000 to improve the operational efficiency of running system services. Previously, each service had its own executable (.exe) file, which made sense at first but eventually led to massive memory consumption and inefficient resource allocation. To resolve this, Microsoft grouped all these services under svchost.exe.
Before svhost.exe, early versions of Windows, such as Windows 95 and Windows NT, relied on individual service executables to handle background tasks. This approach had significant drawbacks, including increased RAM usage and difficulty in managing multiple system processes. With Windows 2000, Microsoft introduced svchost.exe to bundle services with similar functionalities into shared processes. This allowed for more efficient memory utilization and easier management of essential services.
Windows XP and Windows Vista continued to rely heavily on svchost.exe for service management, but users increasingly encountered high CPU usage issues due to multiple services running under a single instance. To address this, Microsoft refined the way services were grouped in later versions of Windows, ensuring that critical services were distributed across different svchost.exe processes to prevent system slowdowns or failures.
In Windows 10 version 1703 and later, Microsoft introduced a major change: systems with over 3.5GB of RAM would automatically run each service in a separate svchost.exe process instead of grouping them together. This improved system stability by preventing a single failing service from crashing an entire svchost.exe process that hosted multiple services. This move also enhanced security by making it harder for malicious software to exploit vulnerabilities in one service and spread to others running in the same process.
This means that for Windows 10 and 11, Microsoft took a more granular approach. Rather than clustering many services together, Windows organized services into smaller, more specialized instances of svchost.exe.
Technical implementation of svchost.exe
Svchost.exe loads dynamic-link libraries (DLLs) and runs them as background services. Instead of each service running independently, they are grouped into instances of svchost.exe based on their function. This reduces memory overhead and allows for better control of system resources.
Functions of svchost.exe
Hosting Windows services
Svchost.exe loads services from DLL files into memory and runs them as part of its process. This helps in conserving system resources as these services share the same instance of svchost.exe.
Examples of services typically hosted by svchost.exe:
- DNS client: Manages DNS lookups and caching for quick internet access.
- Windows update: Handles the downloading and installation of Windows updates.
- Task scheduler: Enables the scheduling and automation of tasks within the operating system.
- Windows audio service: Manages audio playback and input on the system.
- Print spooler: Handles print jobs sent to local and networked printers.
- Windows firewall service: Controls network security and firewall settings.
Resource management
- How svchost.exe manages system resources: By hosting multiple services within a single process, svchost.exe reduces the overall footprint of system resources required for running these services.
- Impact on system performance: Proper management ensures that no single instance consumes more resources than necessary, maintaining system stability and performance. Overloaded svchost.exe instances can, however, sometimes lead to high CPU or memory usage, impacting overall system performance.
- Memory and CPU efficiency: Svchost.exe optimizes how system resources are allocated to background services, ensuring that they only consume the necessary computing power.
- Multi-instance functionality: In newer Windows versions, svchost.exe instances are more distinct, preventing an issue in one instance from affecting others.
Identifying svchost.exe Instances
Since multiple instances of svchost.exe run simultaneously, it’s essential to identify their roles:
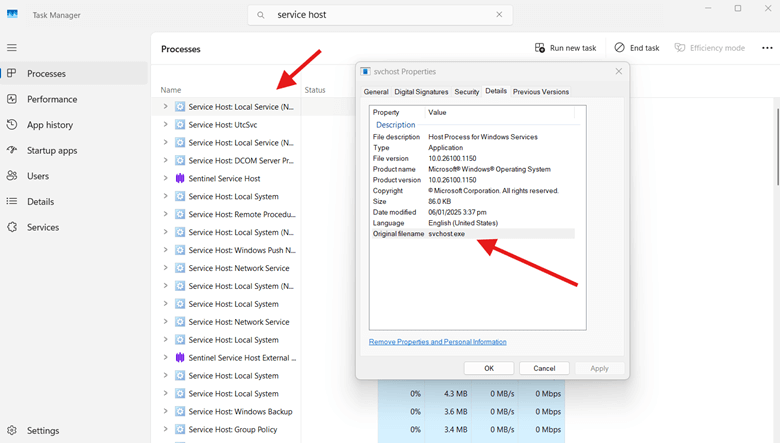
- Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) and go to the Processes tab.
- Locate Service Host: [Service Name] entries.
- Right-click an entry and select Go to Details to see the exact svchost.exe process associated with it.
- Open the Services tab to check which services are running under each instance.
Determining the safety of svchost.exe
Legitimate svchost.exe processes typically reside in the System32 directory of Windows. Any svchost.exe process located elsewhere could be suspect. Monitoring tools can help identify svchost.exe processes that exhibit unusual behavior such as high network usage or unexpected memory consumption.
Tools and methods to verify the authenticity of svchost.exe processes
- Process Explorer: This free tool provides detailed information about which services each svchost.exe instance is hosting.
- Windows Security Center: Built-in Windows security tools can scan and verify the integrity of running processes, including svchost.exe.
How to check the authenticity of a svchost.exe process
While svchost.exe is a legitimate Windows process, malware can disguise itself under the same name. To verify its authenticity:
- Open Task Manager and locate svchost.exe.
- Right-click it and choose Open file location.
- If the file is in C:\Windows\System32, it is genuine. If located elsewhere, it may be malicious.
- Use a reputable antivirus tool to scan for malware.
💡 Check out our guide on the 10 Best Malware Protection Solutions here.

Common signs of svchost.exe-related malware
- Unusual resource consumption: High CPU or memory usage by svchost.exe that doesn’t correlate with known system activities or updates may indicate malicious activity.
- Svchost.exe files running from non-standard locations: Any svchost.exe process executing outside of the C:\Windows\System32 directory should be considered suspicious and possibly malicious.
- Network communications atypical for the services hosted by svchost.exe: Unexpected network activity, such as frequent data transfers or connections to unfamiliar IPs, can be a sign of malware using svchost.exe to mask its operations.
Should you remove svchost.exe?
Removing svchost.exe is a common misconception that can lead to significant system instability and functionality loss. Svchost.exe is crucial for running vital Windows services, and its removal can disrupt essential operations. It is fundamental to system operations, hosting critical services necessary for the proper functioning of the Windows operating system.
However, if you truly are determined to shut down a svchost.exe service, you would need to:
- Proceed to Task Manager.
- Look for the svchost.exe process, right-click it, and select End Task.
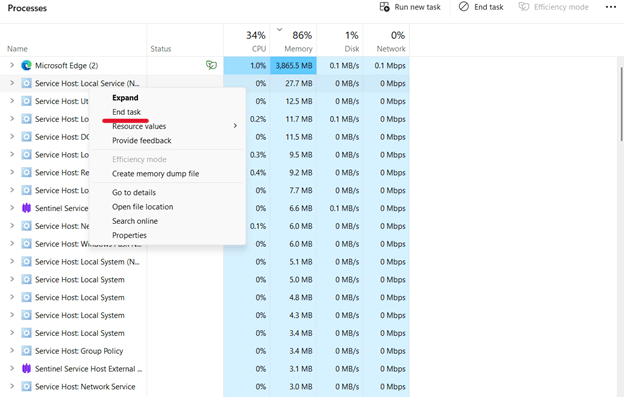
🛑 TAKE NOTE that ending a critical Service Host process can cause system instability.
Alternative solutions for addressing svchost.exe-related issues:
- Deep scan: Conduct a full system scan with antivirus software.
- Wash, rinse, reinstall: In extreme cases, virus infections can still necessitate a full format and clean Windows reinstallation.
- Less is more: Use system configuration tools to disable specific services if they are not necessary.
- Stay current: Update Windows to ensure all security patches and performance improvements are applied.
Steps to take if you suspect a malicious svchost.exe process:
- Confirm the file path of the svchost.exe process.
- Run a malware scan using reputable antivirus software.
- Consult with a professional if malware removal or further analysis is necessary.
Advanced management techniques
For advanced users, managing svchost.exe can improve troubleshooting:
- Use the tasklist /svc command in Command Prompt to list running services.
- Configure specific services to run independently using Services (services.msc).
- Monitor real-time service activity with Process Explorer (a free tool from Microsoft)
You can also troubleshoot a svchost.exe process using Command Prompt.
- Run Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Execute the command sfc /scannow and press Enter. This will automatically scan your computer and repair broken system files. Run the scan up to three times if you keep receiving reports of damaged files.
Troubleshooting high resource usage
Sometimes, svchost.exe may consume excessive CPU or memory. To diagnose and resolve this:
- Use Resource Monitor (search “resmon” in Windows) to see which services are using the most resources.
- If a specific service is being used excessively, consider restarting it using the Services tool (services.msc).
- Disable unnecessary startup services in System Configuration (msconfig).
- Check for pending Windows updates, as update services may cause temporary spikes in resource usage.
- Scan for malware, as certain types of malware disguise themselves as svchost.exe and may hijack system resources.
How to keep svchost.exe secure
- Regular monitoring and updating of security software: Regular monitoring of svchost.exe activities and maintaining up-to-date antivirus software are crucial. Ensure that all Windows updates are applied promptly to mitigate any security vulnerabilities that could be exploited in outdated systems.
- System maintenance and software updates: Regular maintenance, including disk cleanups, system scans, and updating software, can help prevent svchost.exe from becoming a gateway for malware.
- Enabling and configuring Windows Firewall: Proper settings in Windows Firewall can help block unauthorized connections to and from svchost.exe processes, enhancing the security of these vital system components.
Using antivirus and anti-malware software for protection
Robust antivirus programs can detect and remove malicious software masquerading as legitimate svchost.exe processes, providing an essential layer of security. The built-in Windows Defender application is widely considered to be the best free antivirus/anti-malware solution on the market, even outperforming many premium commercial options. For other options, we recommend checking out our list of the 10 best malware protection solutions.
Gain full visibility and control over critical processes such as svchost.exe management with NinjaOne.
Learn more about NinjaOne Endpoint Management solutions
Securing svchost.exe: Insights and implications
Svchost.exe is a critical system process in Windows, essential for managing multiple background services efficiently. Understanding its functionality helps users optimize their systems and recognize potential issues early.
Maintaining the integrity of svchost.exe is paramount for ensuring a secure and stable operating system. Stay vigilant about where svchost.exe processes are running from, monitor their resource usage, and regularly scan your system to ensure no malicious processes are imitating legitimate svchost.exe instances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why are there so many svchost.exe processes running?
Multiple instances of svchost.exe run simultaneously because they host different system services. This segmentation improves system stability and resource management.
- Should I disable svchost.exe?
While you can certainly do so, it’s not recommended. Svchost.exe is essential for running Windows services.
- How can I tell if svchost.exe is malware?
Check its file location in Task Manager. If it’s located in C:\Windows\System32, it is most likely legitimate. If found elsewhere, it may be malicious.
- Why does svchost.exe use so much CPU or memory?
High CPU or memory usage may be due to Windows Update, a malfunctioning service, or malware. Use Resource Monitor and Task Manager to diagnose the issue.
- How do I fix svchost.exe high resource usage?
Restarting the associated service, updating Windows, running a malware scan, and disabling unnecessary services can help resolve high CPU or memory usage.