DNS (Domain Name System) monitoring is an essential task for IT professionals tasked with maintaining network health, security, and performance. DNS serves as the internet’s phonebook, translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers use to communicate. By tracking and analyzing DNS traffic, administrators can ensure the integrity, security, and efficiency of this critical system.
This involves monitoring DNS queries, responses, and the overall performance of DNS servers, which plays a crucial role in detecting anomalies and potential security threats. Ultimately, the main objectives of DNS monitoring are to detect and prevent DNS-based attacks, and to optimize DNS performance for a seamless user experience.
DNS Monitoring with NinjaOne
NinjaOne simplifies DNS monitoring through its integrated platform.
Setting Up a DNS Monitor
1. To add a new device, click the plus sign (+) in the top right corner of the console, then select ‘Device’ from the dropdown menu.
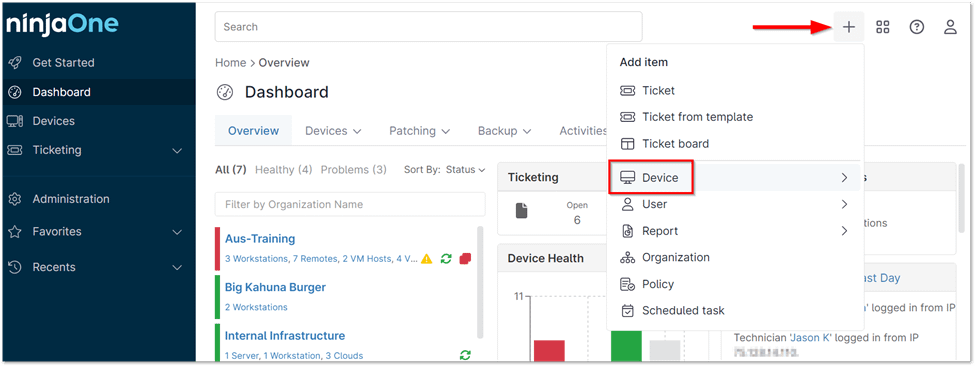
2. Select Cloud monitor.
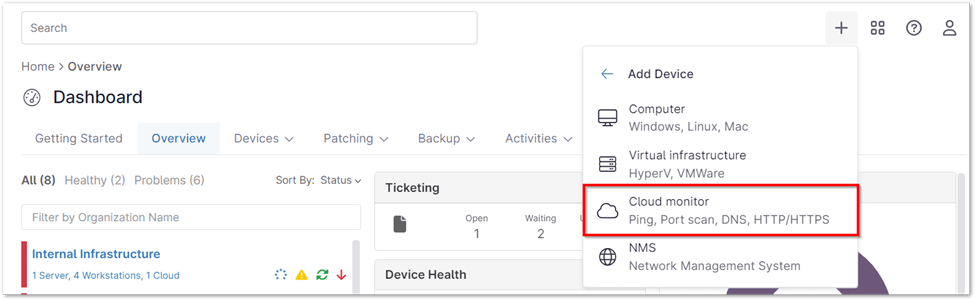
3. Select the desired organization and location for your new cloud monitor. Choose ‘DNS’ as the monitor type, then provide a descriptive display name and fill in any additional required information, such as frequency, timeout, and server settings.
4. Click ‘Next’ to proceed with the setup.
5. Customize your DNS monitor by specifying any conditions you wish to monitor.
There are four types of conditions available for DNS monitoring:
- Query Timed Out: Monitors for instances where the DNS query fails to complete within the expected time frame, indicating a potential timeout.
- No Resolution: Monitors scenarios where the DNS fails to resolve the domain name, which could signal an issue with DNS configuration or availability.
- Record Type: Monitors specific DNS record types to determine whether they contain or do not contain a designated keyword, allowing for precise tracking of DNS record content.
- WHOIS Expiration: Monitors the WHOIS registration information to alert when the domain’s registration is set to expire within a specified number of days.
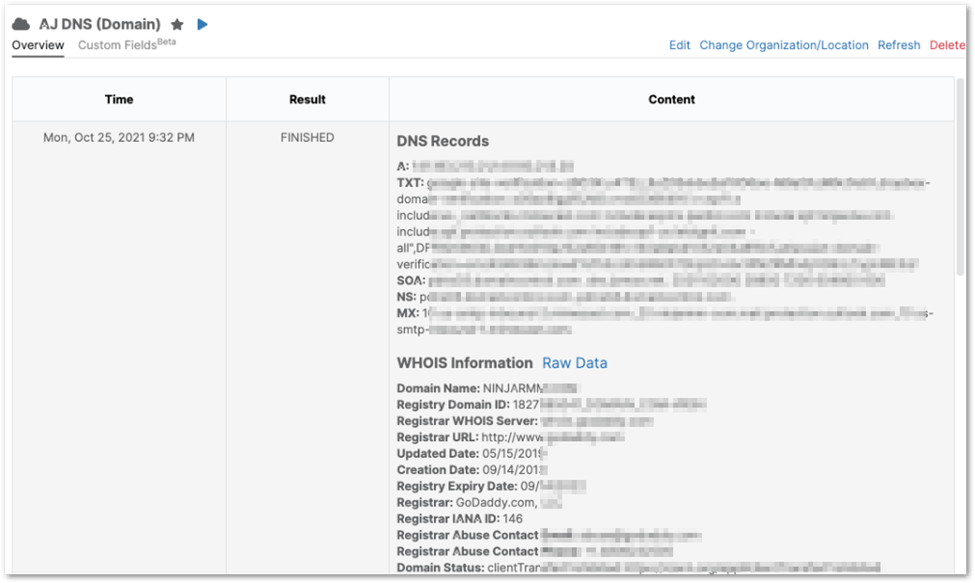
6. Once a DNS cloud monitor is configured, you can review its activity through a table that presents the accumulated data points. This table includes the Time, Result, and Content (including WHOIS information).
Benefits of DNS Monitoring with NinjaOne
- Unified platform: Streamlines DNS monitoring within a broader IT management solution for greater efficiency.
- Ease of use: Intuitive interface allows for quick setup and configuration of DNS monitoring checks, even for non-experts.
- Scalability: Accommodates networks of any size, from small businesses to large enterprises.
- Proactive issue resolution: Real-time insights enable swift action to resolve DNS issues, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
Strategies and Best Practices for DNS Monitoring
- Monitor critical DNS records: Prioritize the monitoring of records crucial to your core services and applications.
- Set appropriate thresholds: Define performance thresholds based on your specific service level agreements (SLAs) and tolerance for downtime.
- Analyze historical data: Leverage reporting and analytics to identify trends, predict potential issues, and optimize your DNS infrastructure.
- Regularly review configurations: Periodically review and update DNS monitoring checks to adapt to changes in your network and services.
Key Applications of NinjaOne DNS Monitoring
- Website Uptime: Monitor ‘A’ records for fast downtime detection and resolution.
- DNS Hijacking Prevention: Use ‘Record Type’ checks to verify ‘A’ record accuracy and detect unauthorized changes.
- Domain Expiration Management: Track ‘WHOIS expires in’ to receive timely renewal reminders and avoid website disruptions.
- Email Delivery Assurance: Monitor ‘MX’ records to ensure email servers are correctly configured and reachable, preventing email delivery issues.
- CDN Performance Optimization: Monitor ‘CNAME’ records associated with Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to identify potential performance bottlenecks and ensure optimal content delivery to users worldwide.