Effective workstation management is key to ensuring the stability, security, and performance of an organization’s IT infrastructure. It involves overseeing end-user devices—desktops, laptops, and other endpoints—across the network, with tasks like patch management, software deployment, remote workstation management, and workstation asset tracking. These functions help minimize security risks and maintain smooth operations.
Proper management, including managing workstation inventories, keeps devices secure, up-to-date, and functional, reducing downtime and vulnerabilities. It also enables IT teams to quickly address issues across diverse operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux.
By centralizing these tasks with workstation management software, organizations gain better control, enhance productivity, and streamline operations, ensuring security, compliance, and efficiency. Managed workstations help optimize device performance and facilitate proactive support.
How to Manage Your Workstation Using NinjaOne?
This is a comprehensive guide to help you manage and optimize your workstations, whether you’re configuring new endpoints or maintaining existing ones through NinjaOne’s workstation management platform.
Linux
NinjaOne’s Linux policy management feature is essential for IT administrators to efficiently monitor, manage, and secure Linux endpoints at scale.
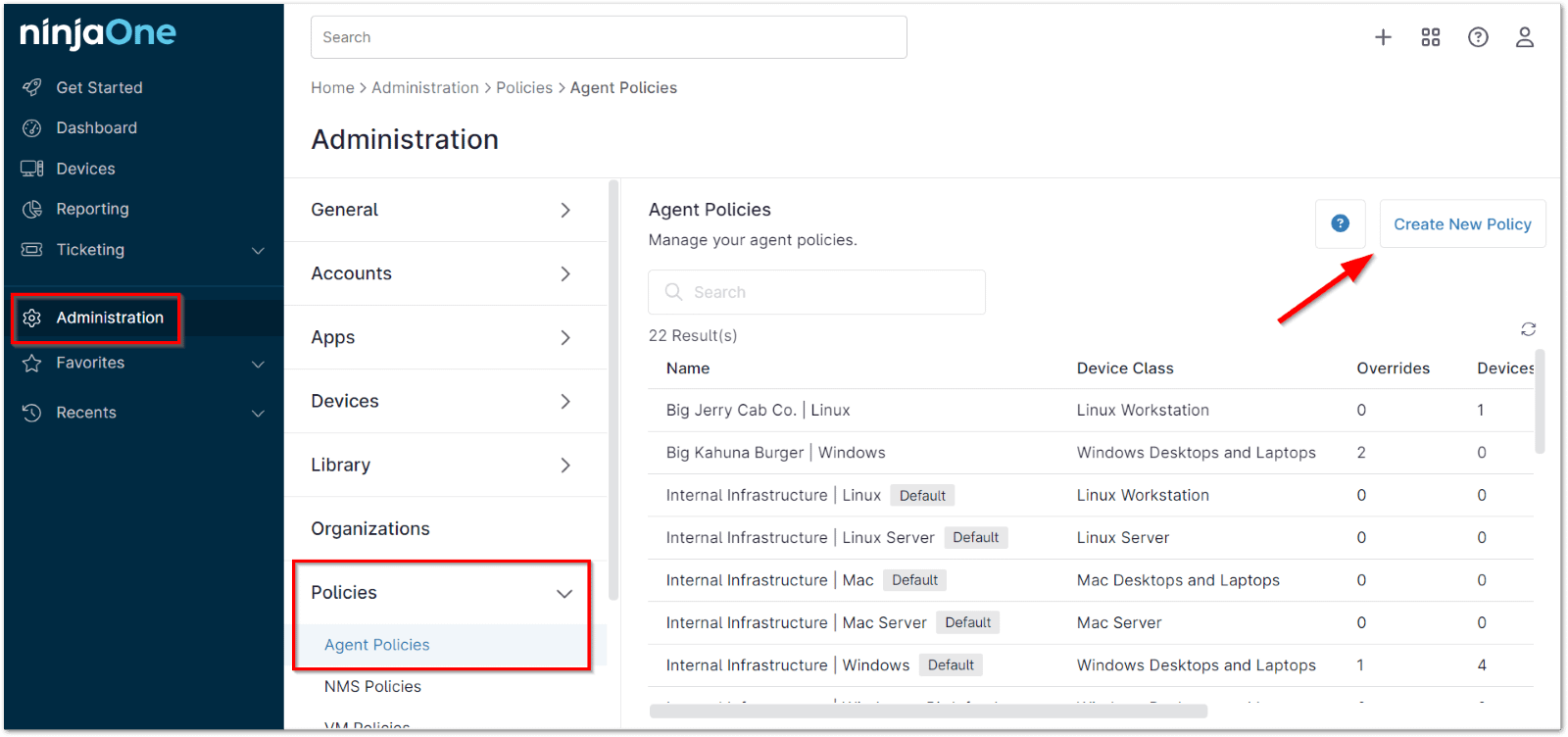
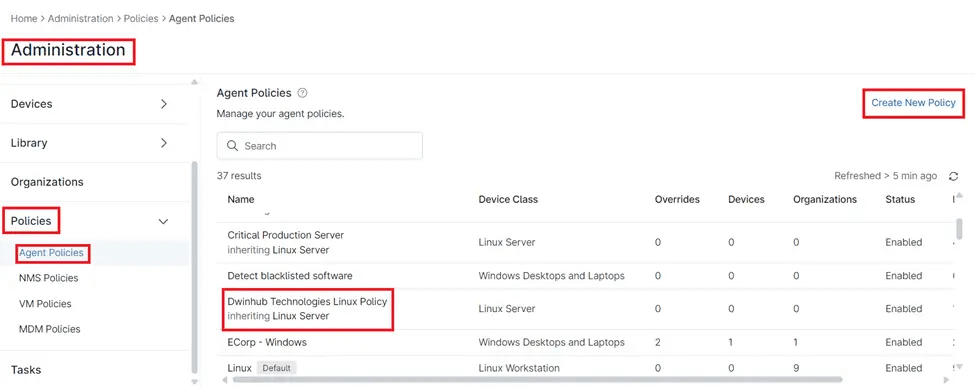
- Access the “Administration” Section:
- From the NinjaOne dashboard, navigate to the left-hand sidebar.
- Click on “Administration” to expand the options under this section.
- Navigate to “Policies”:
- Under the Administration section, locate and click on “Policies” to reveal the different policy categories.
- Select “Agent Policies”:
- Click on “Agent Policies” from the list of policy categories. This will display the list of all existing agent policies on the right-hand side.
- Create or Edit a Policy:
- To create a new Linux policy, click on the “Create New Policy” button located at the top-right corner of the Agent Policies page.
- To edit an existing Linux policy, locate the desired policy from the list and click on it.
When configuring the NinjaOne Linux Policy for your workstation, the following policy settings are available:
- Conditions: Conditions are defined at the policy level, enabling IT administrators to proactively monitor their systems with minimal configuration. When a condition matches the predefined criteria—such as missing software or memory thresholds—NinjaOne can automatically assign a severity and priority, send notifications to designated recipients, trigger automations, and/or create a support ticket.
- Scheduled Automations: Scheduled automations allow you to execute actions from your Automation Library on endpoints (i.e., devices) associated with a policy. These automations can be triggered either on-demand or at scheduled intervals.
- Patching: Patch management software, such as that included with NinjaOne, gives users a complete, centralized view of their patch compliance rate and automates the identification, downloading, and deployment of patches across your managed devices.
- Antivirus: NinjaOne integrates with several third-party antivirus solutions, including Bitdefender GravityZone, CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, and Webroot.
- Activities: Policy activities allow you to enhance and create alert, visibility, and safety options around specific endpoint events.
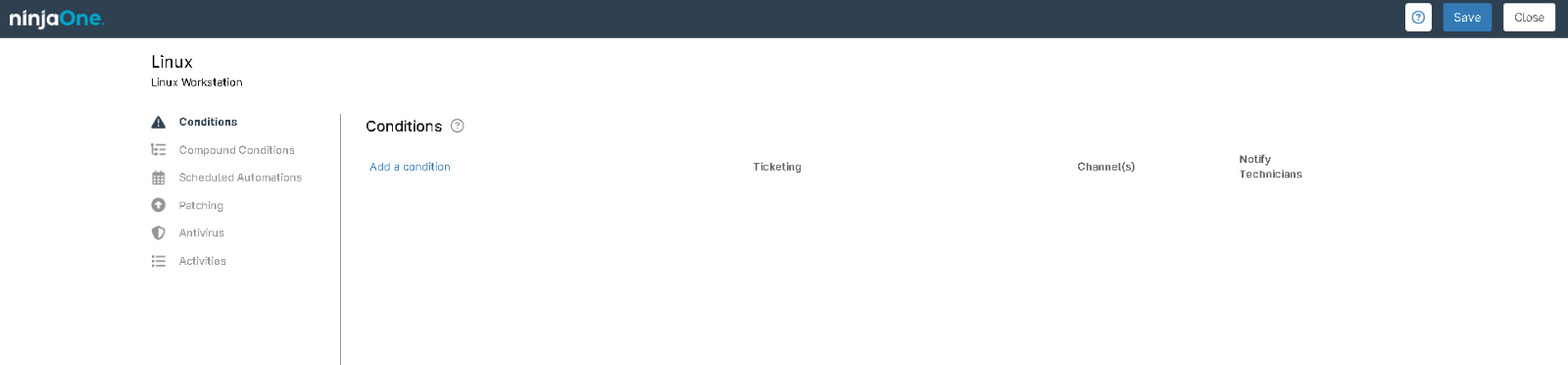
This comprehensive guide details NinjaOne’s Linux policy features: Linux Policy
Mac
NinjaOne’s Mac policy management feature enables IT administrators to efficiently control, secure, and ensure compliance across Apple devices, including managing app distribution, network access, and data encryption.
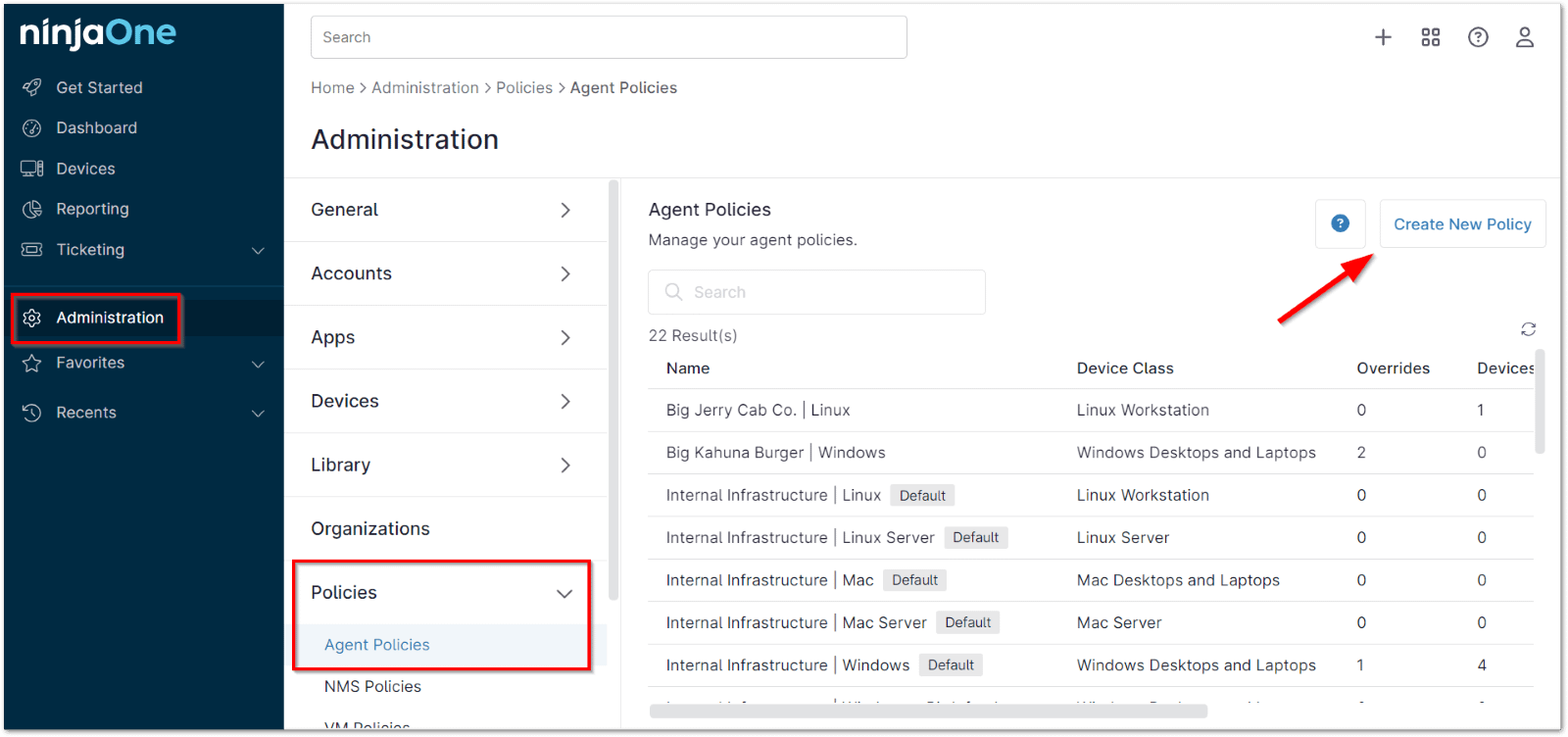
- Access the “Administration” Section:
- From the NinjaOne dashboard, navigate to the left-hand sidebar.
- Click on “Administration” to expand the options under this section.
- Navigate to “Policies”:
- Under the Administration section, locate and click on “Policies” to reveal the different policy categories.
- Select “Agent Policies”:
- Click on “Agent Policies” from the list of policy categories. This will display the list of all existing agent policies on the right-hand side.
- Create or Edit a Policy:
- To create a new Mac policy, click on the “Create New Policy” button located at the top-right corner of the Agent Policies page.
- To edit an existing Mac policy, locate the desired policy from the list and click on it.
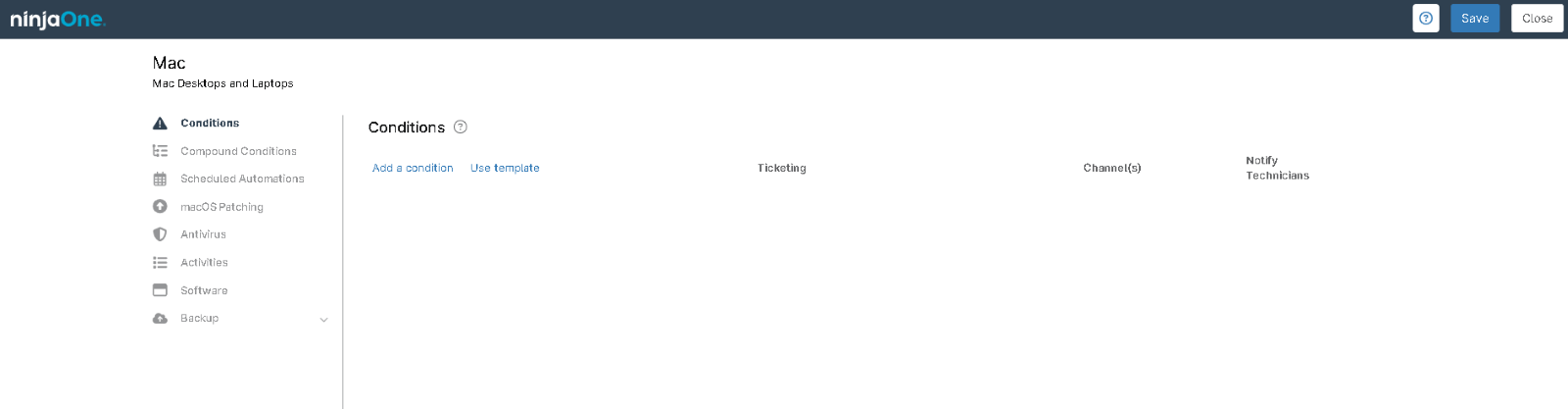
When configuring the NinjaOne Mac Policy for your workstation, the following policy settings are available:
- Conditions: Conditions are defined at the policy level, enabling IT administrators to proactively monitor their systems with minimal configuration. When a condition matches the predefined criteria—such as missing software or memory thresholds—NinjaOne can automatically assign a severity and priority, send notifications to designated recipients, trigger automations, and/or create a support ticket.
- Scheduled Automations: Scheduled automations allow you to execute actions from your Automation Library on endpoints (i.e., devices) associated with a policy. These automations can be triggered either on-demand or at scheduled intervals.
- Windows Patches: Patch management software, such as that included with NinjaOne, gives users a complete, centralized view of their patch compliance rate and automates the identification, downloading, and deployment of patches across your managed devices.
- Antivirus: NinjaOne integrates with several third-party antivirus solutions, including Bitdefender GravityZone, CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, and Webroot.
- Activities: Policy activities allow you to enhance and create alert, visibility, and safety options around specific endpoint events.
- Software: The Software tab allows you to configure software patch management and automatically push specific software to your devices.
- Backups: Backups allow you to configure and manage automated data backups for your devices, ensuring that your data is consistently saved and can be easily restored in case of an emergency.
This comprehensive guide details NinjaOne’s Mac policy features: Mac Policy
Windows
NinjaOne’s Windows policy management feature empowers IT administrators to effectively control, secure, and maintain compliance across Windows devices, including managing software distribution, network settings, and data protection.
- Access the “Administration” Section:
- From the NinjaOne dashboard, navigate to the left-hand sidebar.
- Click on “Administration” to expand the options under this section.
- Navigate to “Policies”:
- Under the Administration section, locate and click on “Policies” to reveal the different policy categories.
- Select “Agent Policies”:
- Click on “Agent Policies” from the list of policy categories. This will display the list of all existing agent policies on the right-hand side.
- Create or Edit a Policy:
- To create a new Windows policy, click on the “Create New Policy” button located at the top-right corner of the Agent Policies page.
- To edit an existing Windows policy, locate the desired policy from the list and click on it.
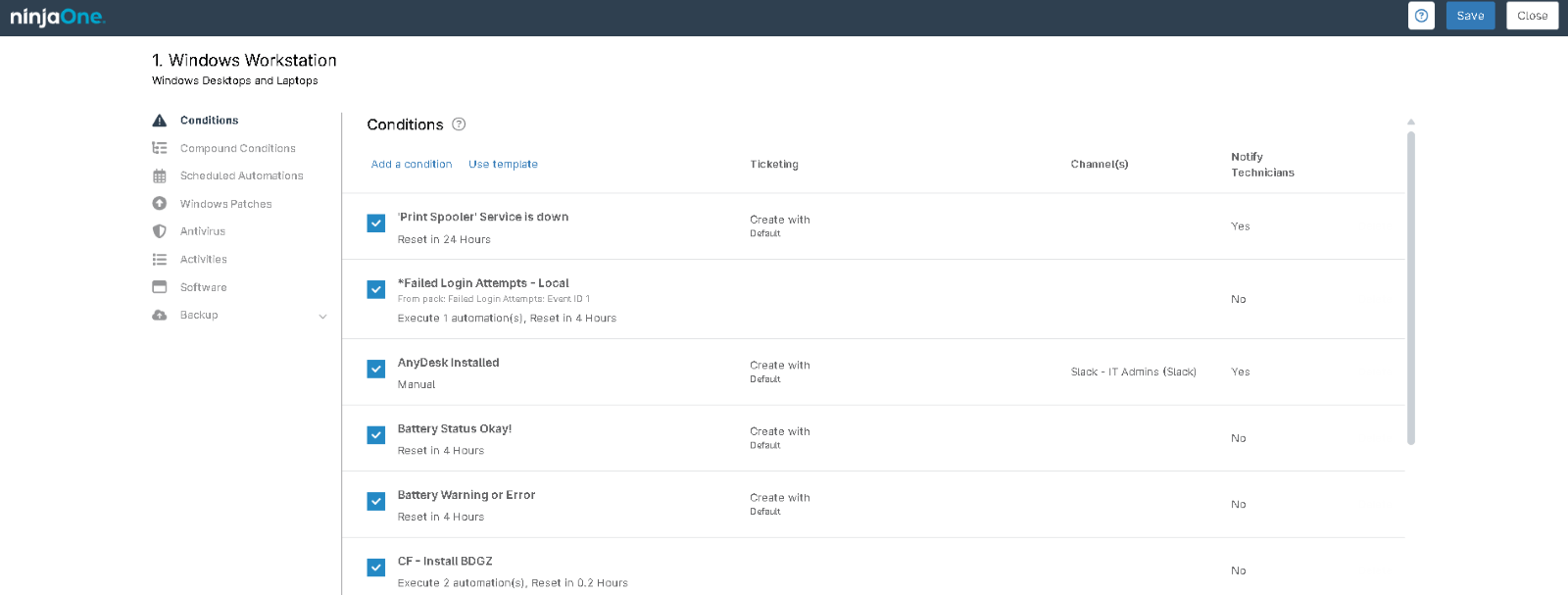
When configuring the NinjaOne Windows Policy for your workstation, the following policy settings are available:
- Conditions: Conditions are defined at the policy level, enabling IT administrators to proactively monitor their systems with minimal configuration. When a condition matches the predefined criteria—such as missing software or memory thresholds—NinjaOne can automatically assign a severity and priority, send notifications to designated recipients, trigger automations, and/or create a support ticket.
- Scheduled Automations: Scheduled automations allow you to execute actions from your Automation Library on endpoints (i.e., devices) associated with a policy. These automations can be triggered either on-demand or at scheduled intervals.
- Windows Patches: Patch management software, such as that included with NinjaOne, gives users a complete, centralized view of their patch compliance rate and automates the identification, downloading, and deployment of patches across your managed devices.
- Antivirus: NinjaOne integrates with several third-party antivirus solutions, including Bitdefender GravityZone, CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, and Webroot.
- Activities: Policy activities allow you to enhance and create alert, visibility, and safety options around specific endpoint events.
- Software: The Software tab allows you to configure software patch management and automatically push specific software to your devices.
- Backups: Backups allow you to configure and manage automated data backups for your devices, ensuring that your data is consistently saved and can be easily restored in case of an emergency.