An audit log is a detailed record of events, actions, and changes occurring within a system or software environment. It provides a chronological record of activities, offering valuable insights into user behavior, system modifications, and potential security breaches. In the context of Mobile Device Management (MDM), an MDM audit log viewing specifically tracks actions related to device management, policy assignment, remote actions, configuration changes, and more.
This information is crucial for maintaining compliance, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring the security of managed devices. NinjaOne provides a robust audit log viewer that allows IT administrators to efficiently monitor and analyze these activities across all managed endpoints.
How to View Audit Logs with NinjaOne
NinjaOne makes accessing and reviewing audit logs straightforward:
1. Access the NinjaOne Dashboard: Log in to your NinjaOne account and navigate to the main dashboard.
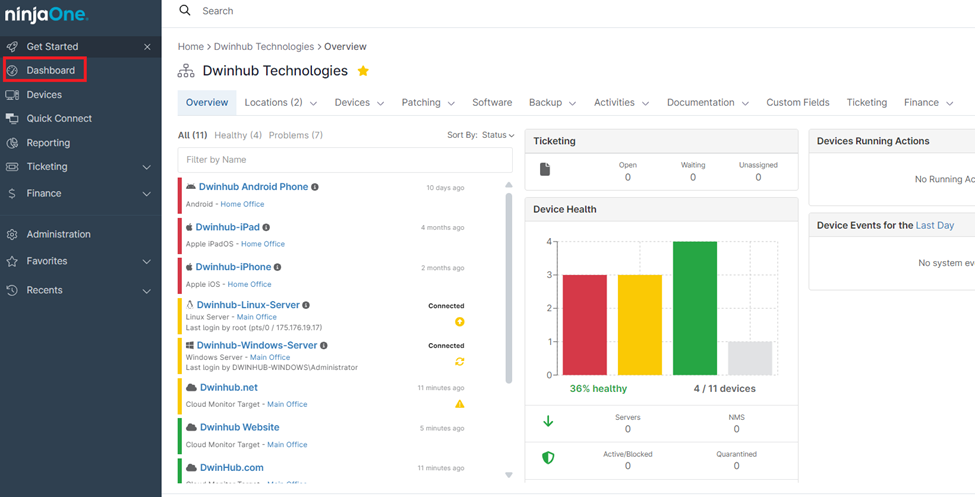
2. Select the Organization: Choose the organization that contains the device you want to audit. This helps narrow down your search and focus on a specific set of devices.
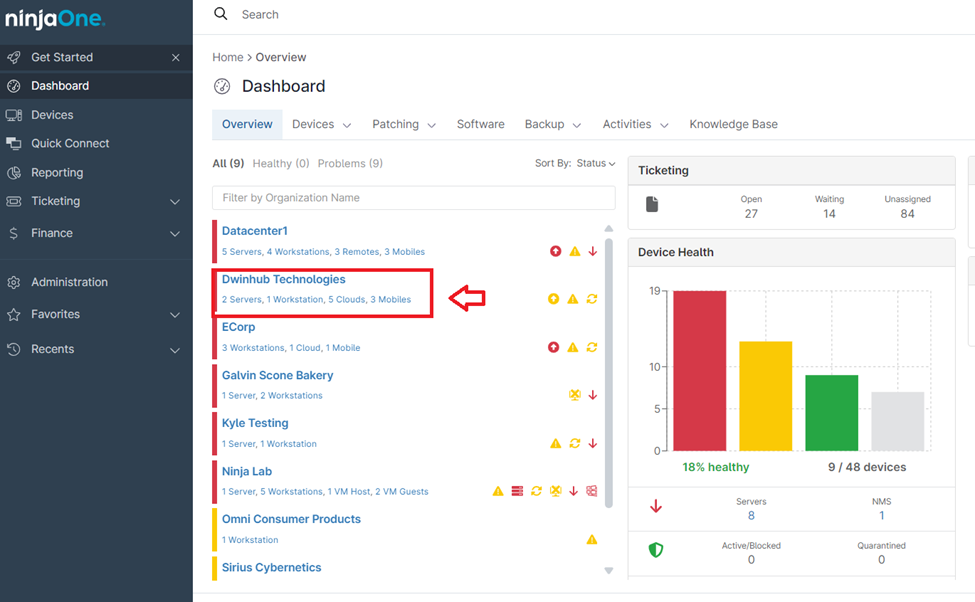
3. Select the Device: Choose the specific device for which you want to view the audit log. You can do this by searching for the device name or browsing through your device inventory within the selected organization.
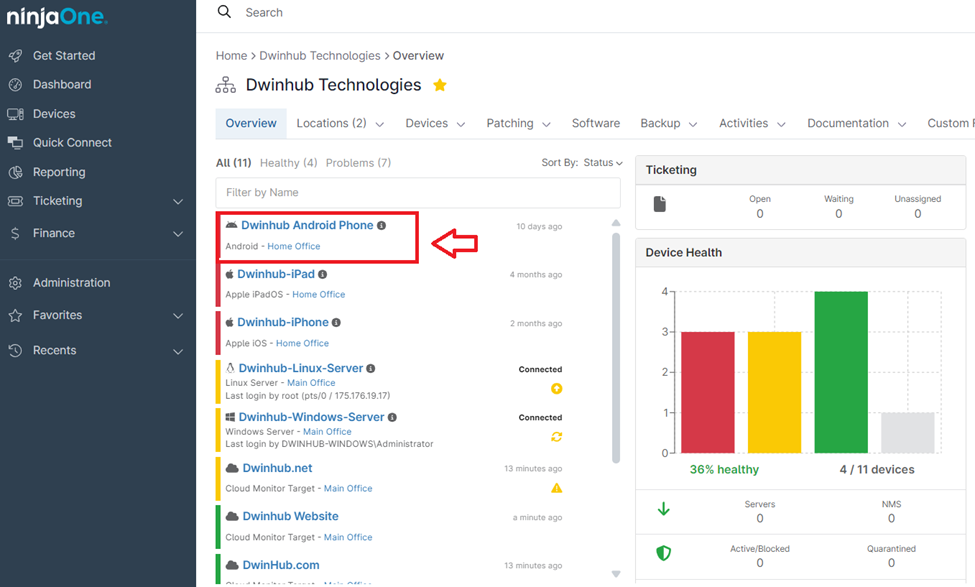
4. Navigate to the Activities Tab: Once you’ve selected the device, click on the “Activities” tab. This will display a comprehensive list of all logged events associated with that device.

5. Filter and Search: Utilize the filtering and search options to refine the audit log view. You can filter by event type, date range, user, and more. This allows you to quickly pinpoint specific activities or investigate potential issues.
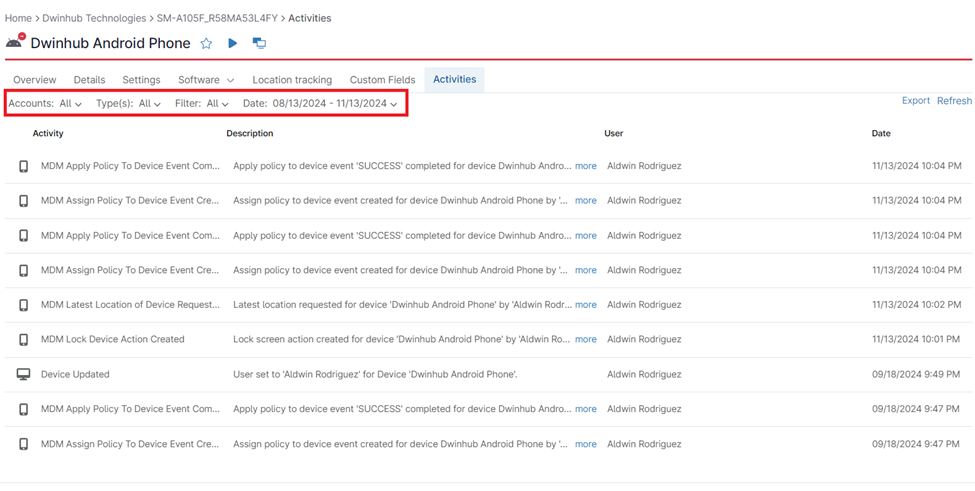
Activities Monitored by NinjaOne MDM Audit Logs
Here are some of the activities tracked in NinjaOne MDM audit logs:
- Device Creation: The creation of new device records within the MDM system is logged, providing a history of device enrollment.
- Device Updates: Any modifications made to device details are logged with the user responsible for the update. This includes changes to device ownership and other device properties.
- Policy Assignment and Application: The audit log tracks all activities related to policy assignment, such as when a policy is assigned to a device, when changes are made to existing policies, and the status of policy application. This includes the creation of policy assignment events and the completion of policy application events.
- Device Lock Actions: Any action related to locking a device is recorded, including the initiation of a lock command, the success or failure of the action, the user who triggered it, and any updates to the lock action status.
- Device Location Requests: NinjaOne logs each instance when a device’s location is requested by an administrator. This includes details about the requester, the device targeted, and the timestamp of the request.
The Benefits of Using NinjaOne for Audit Log Viewing
NinjaOne offers several advantages when it comes to audit log management:
- Centralized View: Access all device activity logs from a single, unified dashboard, simplifying audit log management across your entire endpoint environment.
- Granular Detail: NinjaOne captures a wide range of events, providing in-depth information about user actions, system changes, and policy deployments.
- Powerful Filtering and Search: Easily sift through extensive logs with flexible filtering and search capabilities, saving time and effort during investigations.
Strategies for Audit Log Management with NinjaOne
- Regularly Review Logs: Establish a routine for reviewing audit logs to proactively identify potential issues and ensure the health of your IT environment.
- Define Alerting Rules: Configure alerts to notify you of critical events or suspicious activities, enabling rapid response to potential threats.
- Utilize Filtering for Investigations: Leverage filtering options to narrow down log entries when troubleshooting problems or investigating specific incidents.
Examples of Audit Log Use Cases
- Troubleshooting: Identify the root cause of a device issue by examining the sequence of events leading up to the problem.
- Security Monitoring: Detect unauthorized software installations or configuration changes that might indicate malicious activity.
- Compliance Audits: Gather evidence of policy enforcement, software deployments, and user activity to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
