What are applicable patches?
Applicable patches refer to software updates or fixes that are relevant and necessary for a particular system or application. These patches are designed to address security vulnerabilities, performance issues, or bugs within the software.
Applying patches is crucial for maintaining the security and stability of systems and applications, as they help to close potential avenues for cyberattacks and prevent system malfunctions. Patch management involves identifying which patches are applicable to a particular system or environment, testing them to ensure compatibility and stability, and then deploying them in a timely manner.
Failure to apply applicable patches can leave systems vulnerable to exploitation by malicious actors or result in performance degradation or system failures. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to have robust patch management practices in place to keep their systems up to date and secure.
There are two main contexts where you might encounter “applicable patches”:
- Patch Management Tools: Many patch management programs have a section that displays applicable patches. This section lists the updates recommended for your specific environment, helping you prioritize which ones to install.
- Patch Reports: Patch reports generated by IT systems may also highlight applicable patches. These reports identify missing updates that could leave your systems vulnerable.
How can you identify the applicable patches on a system?
Normally, to identify the applicable patches, a scan process needs to be performed on the system, and this takes time. After the scan has completed, the list of applicable patches along with the patch details is generated. If there´s more than one system, this process needs to be repeated on each of the systems. As the number of systems increases, this process gets more complicated and time consuming, this is why an automated patch deployment system, like NinjaOne is preferred, which instructs the systems to perform the process in the background without human intervention.
How can NinjaOne help to identify applicable patches on a system?
The applicable patches for a system can be listed after a scan process, NinjaOne can scan for patches either manually by running a scan automation or automatically using a policy.
Manual scan: NinjaOne has a native scan automation that is easy to use, follow the next instructions to run it.
- Go to Your organization dashboard.
- Find the target computer for which you want to run the scan automation; you can use filters to assist with the search.
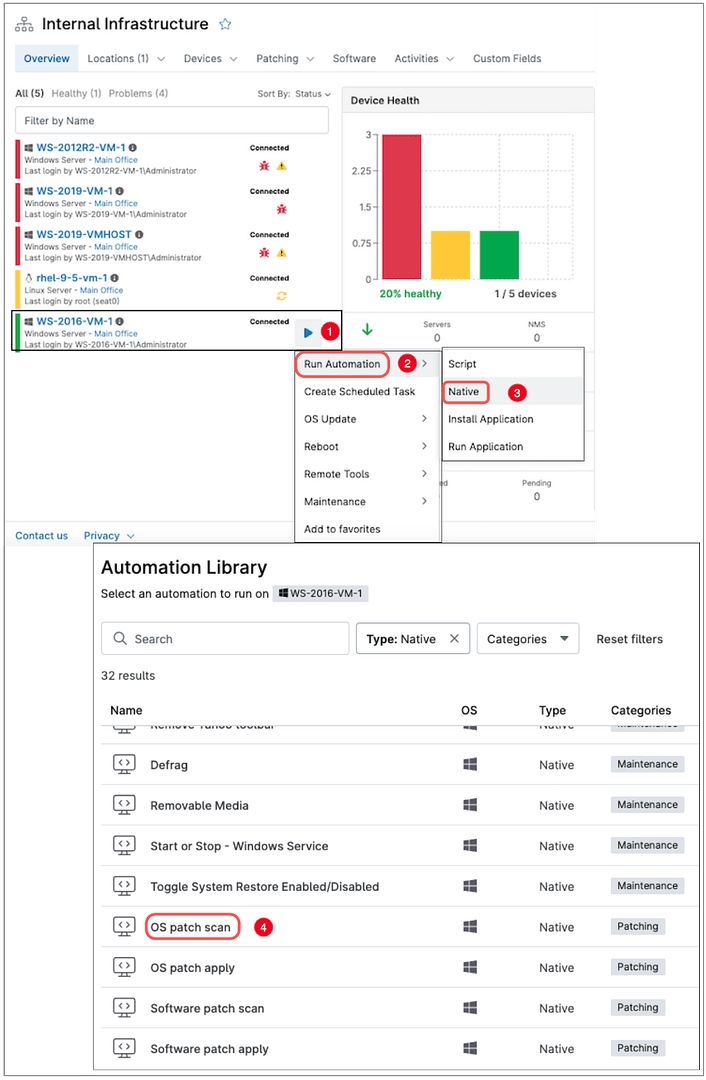
- Hover over the target computer until a blue arrow appears to the right of its name. Move the mouse pointer over the blue arrow to reveal a drop-down menu. Next, hover over Run Automation to display another menu, then click Native. This will open the Automation Library, where you can select OS Patch Scan.
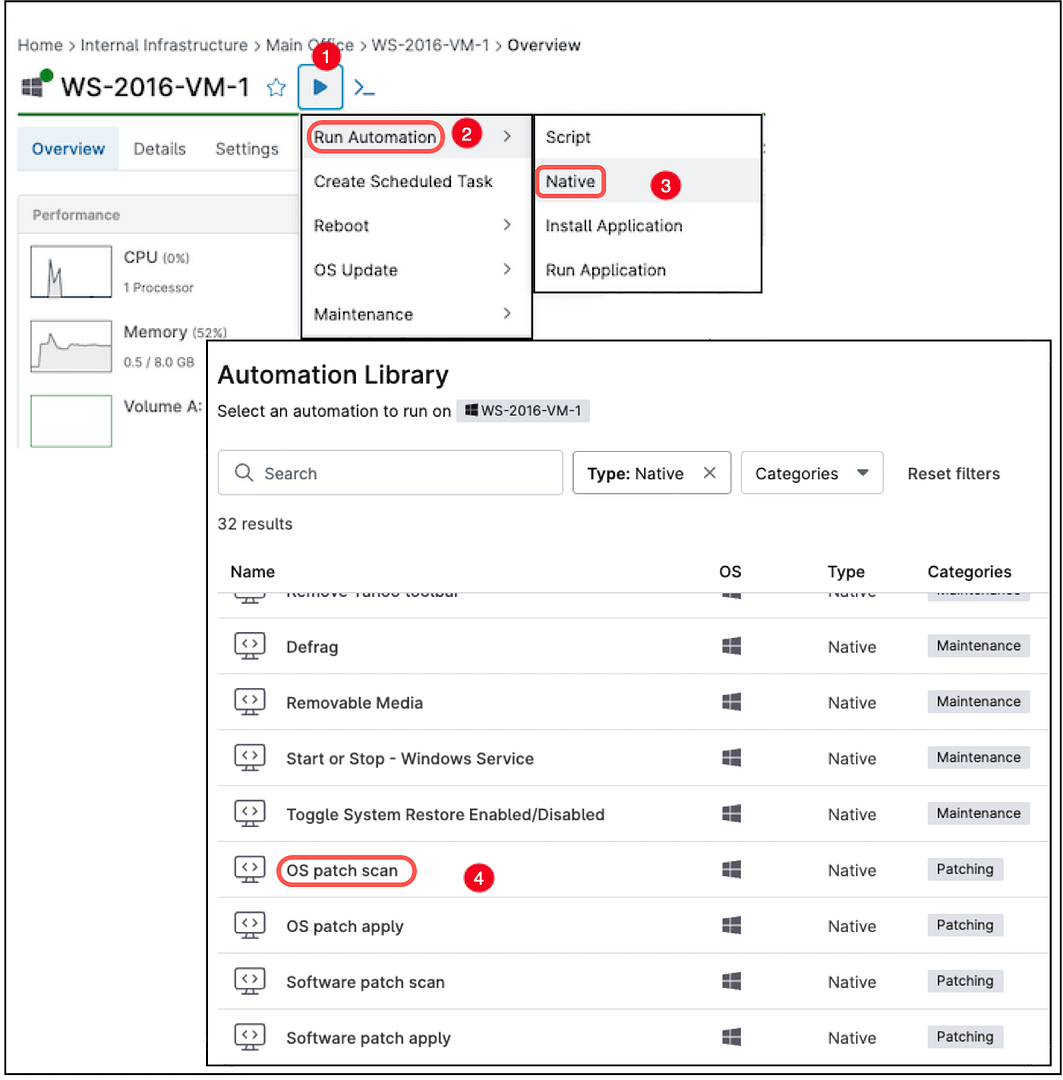
Alternatively, click on the target computer name to open a new window with device details. A blue arrow will appear to the right of the device name. Hover over the blue arrow to display a drop-down menu, then hover over Run Automation to reveal another drop-down. Click Native to open the Automation Library, where you can select OS Patch Scan.
Another way to run a manual scan is by hovering the mouse over OS Update (instead of Run Automation) and then click on Scan.
Automatic scan: If you have a policy for automated patching, the scan process happens in the background at the configured schedule, then the patch installation and reboot will happen at the scheduled time defined in the policy.
How to make sure all applicable patches are installed using automation?
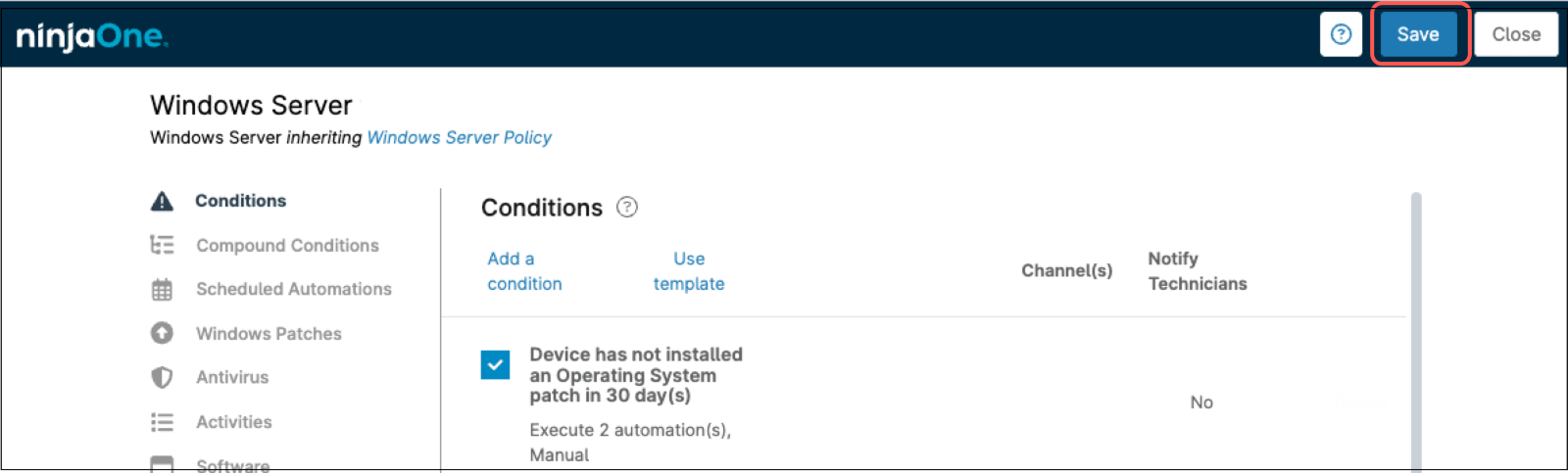
By using policies and properly configuring the patching section we can schedule patch scan, patch install and reboots, however, if for any reason the scan/install window was missed, we can add a condition which detects when the last OS patch installed has passed some period and run an OS patch scan and an OS patch install automation. Follow the steps below to configure this automation in a Windows policy.
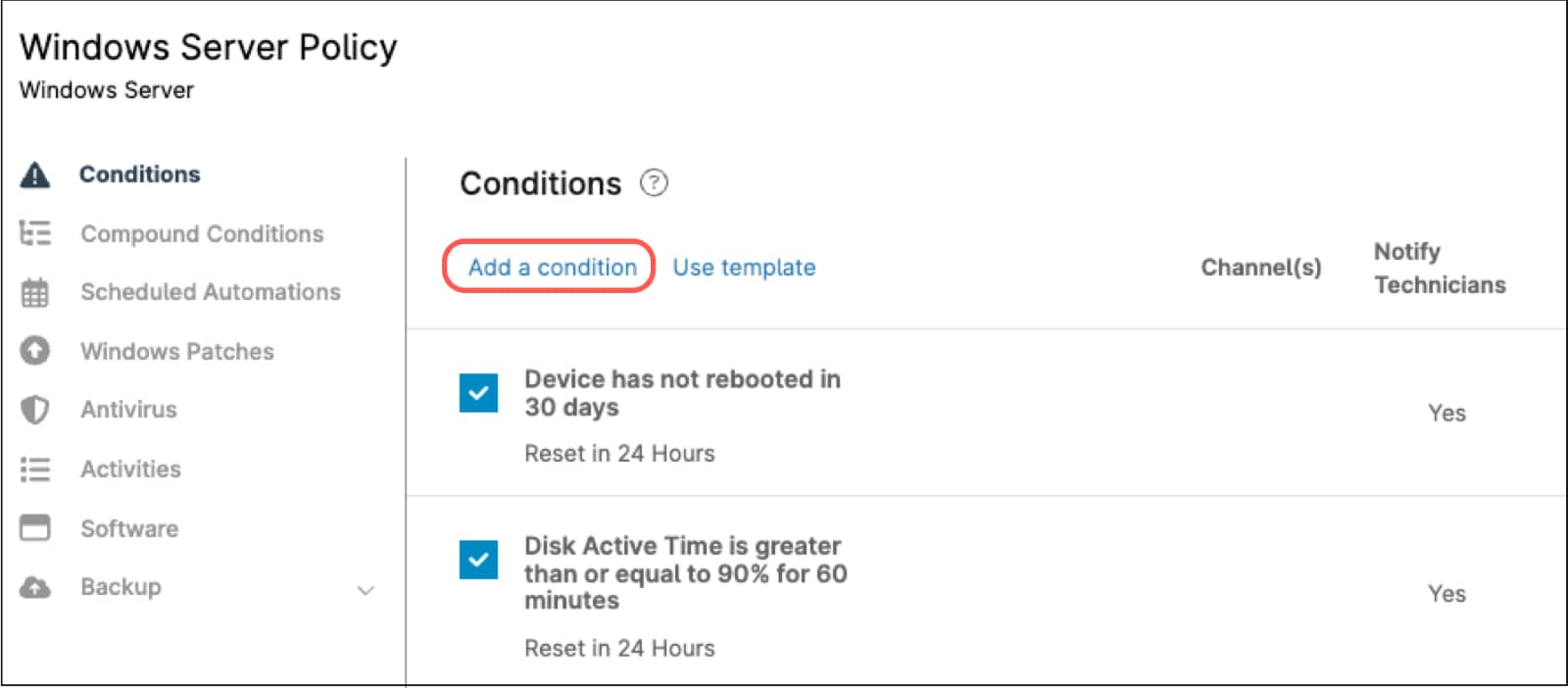
- Select the policy of your preference to add this automation and open the policy editor.
- Click Add a condition. The condition editor appears.
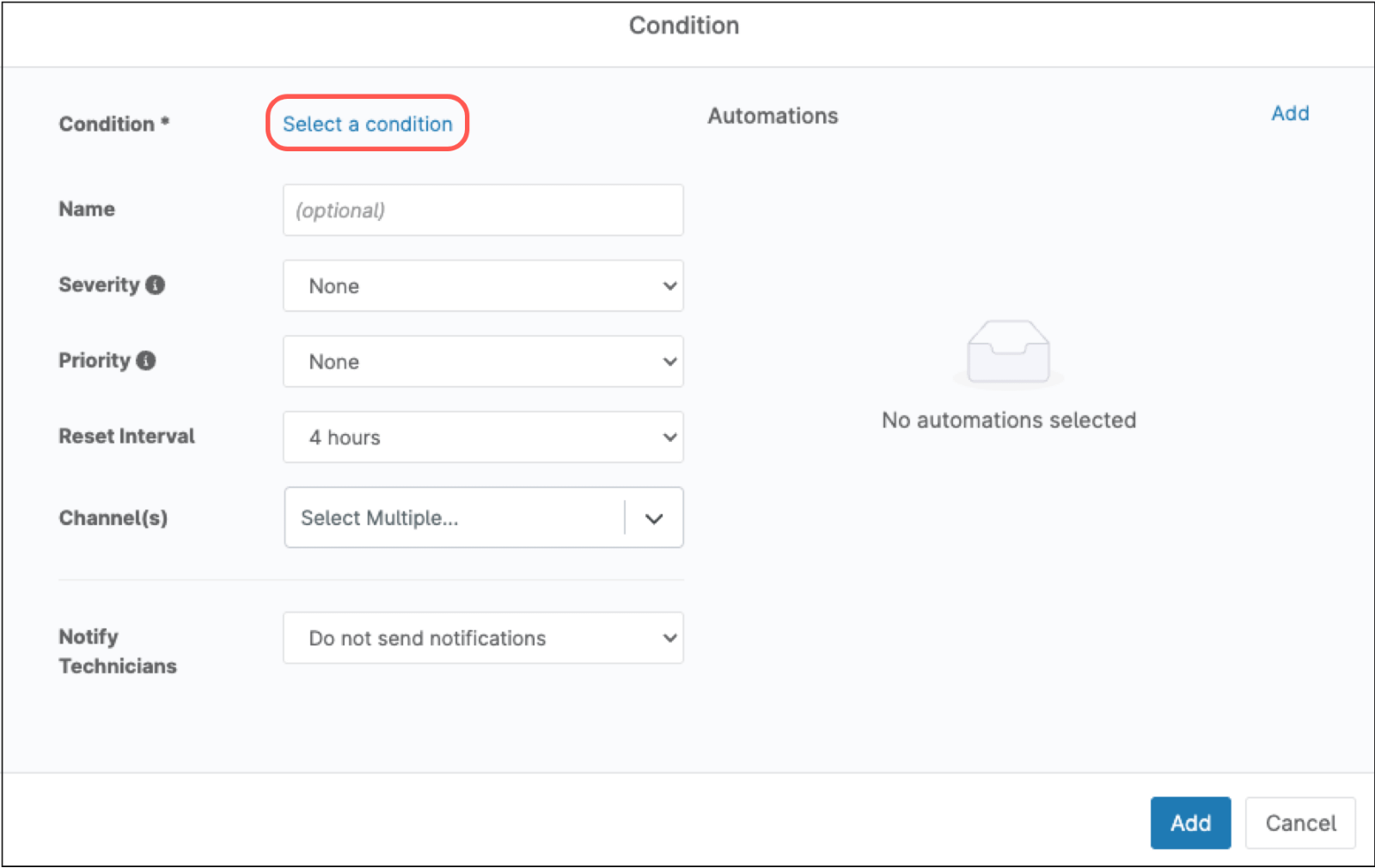
- Click Select a condition.
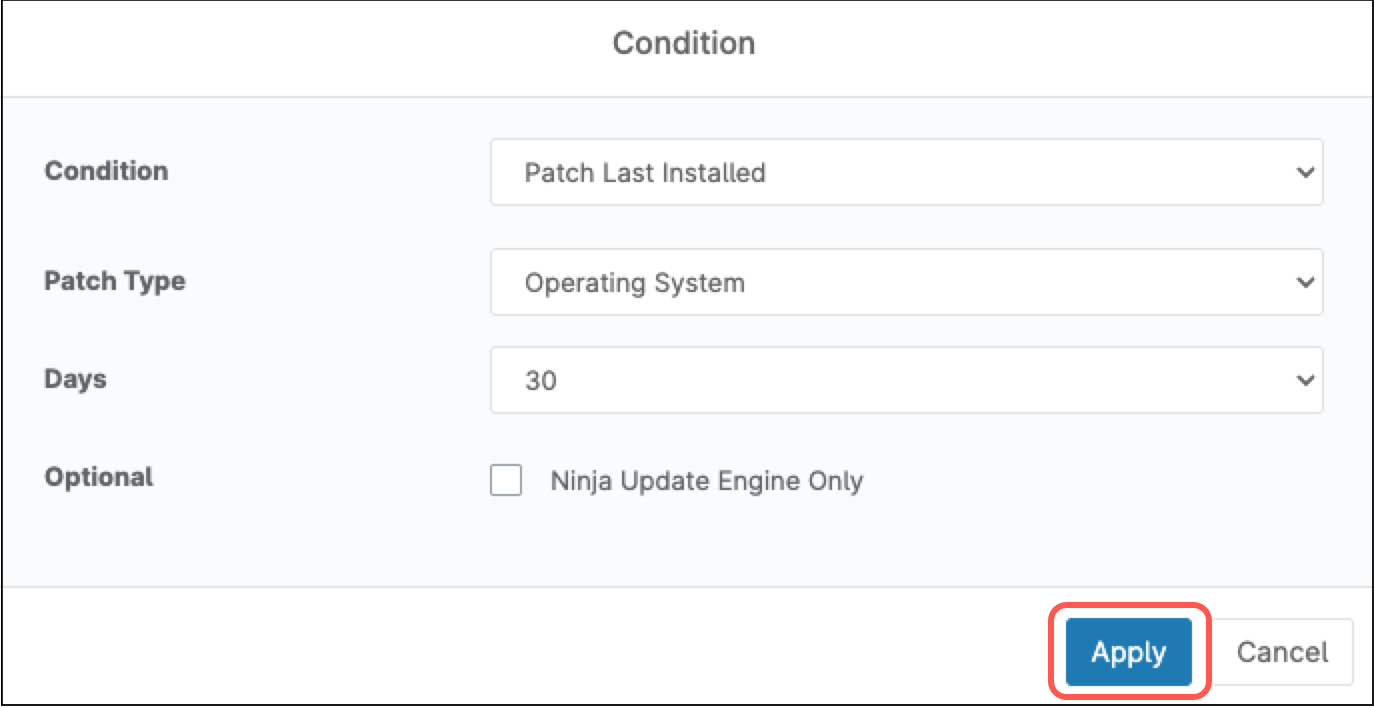
- From the Condition drop-down, select Patch last installed.
- Under Patch type, select Operating system.
- Under days, select your preferred limit, for instance, 30 (which means 30 days without installing OS patches).
- Click Apply.
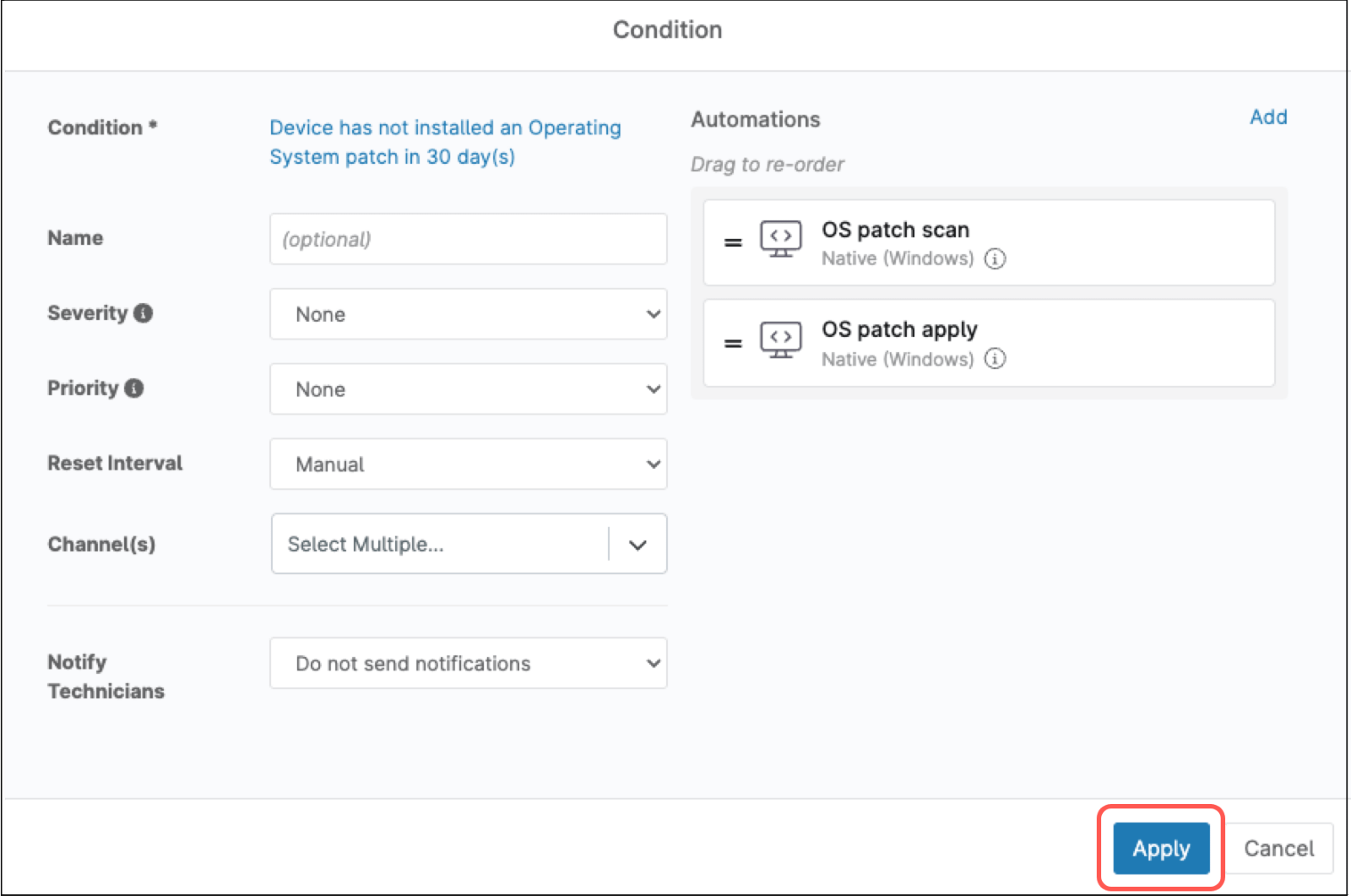
- On the right side of the policy editor, under the Automations section, click Add. The automation library appears.
- Select OS patch scan, the automation appears under Automations.
- On the right side of the policy editor, under the Automations section, click Add again. The automation library appears.
- Select OS patch apply, the automation appears under Automations.
- Click the blue Add button at the bottom of the policy editor.
- Save the changes made to the policy.
Note: The reboot is controlled by the reboot options in the policy.