NinjaOne OS Patching for Streamlined IT Operations
NinjaOne revolutionizes OS patching by delivering a streamlined, automated approach that empowers IT teams to deploy critical updates without the headaches.
Whether managing Windows, Mac, or Linux environments, NinjaOne provides a single, powerful platform to patch devices quickly, securely, and reliably. Say goodbye to patching delays and vulnerabilities with a solution built for today’s fast-paced IT world.
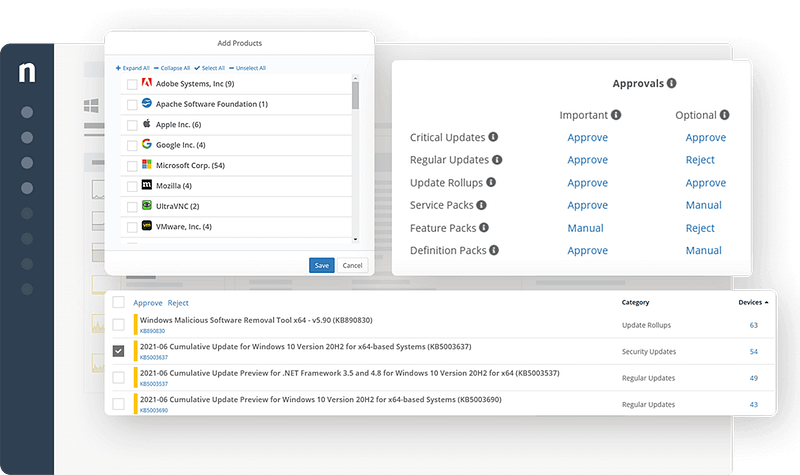
Why NinjaOne Makes OS Patching effortless and reliable
Automated Operating System Patches without the complexity
Centralized Visibility into OS Patches across all devices
Customizable Patching Policies for complete control
Patch Faster, Patch Smarter with minimal disruptions
Integrated Reporting for better compliance and audits
Secure Patching Operating System Updates through trusted channels
Discover the robust features that streamline patch management
Automated Patch Detection and Deployment
Cross-Platform OS Patching in Windows, Mac, and Linux
Flexible Patch Scheduling and Maintenance Windows
Dynamic Device Grouping for Targeted Patching
Patch Approval Workflows for Quality Assurance
Granular Role-Based Access Control
Powerful patch management for every business need
Enterprise Environment Management
Seamless OS Level Patching for Distributed Workforces
Patch Management and Compliance for MSPs and IT Providers
Protect your environment, increase operational efficiency, and simplify patch management with NinjaOne!
OS Patching FAQs
What is OS Patching?
OS patching refers to the process of updating the operating system (OS) on a device to ensure it remains secure, stable, and up-to-date. This process involves deploying patches or updates that fix vulnerabilities, address bugs, and introduce new features. OS patching is crucial for maintaining the overall health and security of a system, as outdated OS versions can leave devices vulnerable to attacks.
Why is OS Patching Important?
OS patching is vital because it helps protect systems from security breaches, data loss, and other risks that may arise from outdated software. Regular patching ensures that both OS patching in Linux and OS patching in Windows is up to date with the latest security fixes. Without timely updates, devices become susceptible to malware, ransomware, and other cyber threats that can disrupt business operations.
How to Check OS Patch Level in Windows?
To check the OS patch level in Windows, you can go to the “Settings” menu, select “Update & Security,” and then click on “Windows Update.” Here, you can see the update history, which will show the most recent updates installed, including security patches.
How to Check OS Patch Level in Linux?
In Linux, checking the OS patch level depends on the distribution you are using. For most distributions, you can use the terminal and type commands like:
Debian/Ubuntu: sudo apt list –upgradable
Red Hat/Fedora (modern): sudo dnf check-update
Legacy Red Hat/CentOS 7: sudo yum check-update
These commands will display any available updates, including patches for the operating system.
What is the difference between manual OS patching versus automated OS patching?
The main difference between manual OS patching versus automated OS patching lies in how the patches are applied and managed. Manual OS patching requires IT administrators to check for updates and apply them manually, often involving significant time and effort to ensure all devices are updated. This method can be error-prone, as it depends on human intervention to stay consistent and timely. In contrast, automated OS patching streamlines the process by scheduling and deploying updates without manual input.
This method is more efficient, reducing the risk of human error, ensuring patches are applied promptly, and maintaining system security across large fleets of devices. Automated OS patching is particularly useful in environments where managing multiple systems is required, ensuring that patches are applied consistently across all devices.
Related Resources
8 Patch Management Best Practices
Learn the best practices in patch management to protect your systems from cyberattacks.
How to Uninstall a Problematic Patch: A Step-By-Step Guide
Explore ways to resolve vulnerabilities by uninstalling problematic patches.
Best Patch Management Softwares for MSPs and IT


