NinjaOne Remote Troubleshooting Software Enhances IT Efficiency
IT teams need powerful remote troubleshooting software to resolve issues quickly and securely. Legacy tools often struggle to keep up with modern IT demands, lacking the flexibility and seamless experience needed for fast problem resolution.
NinjaOne’s remote troubleshooting software integrates secure remote desktop access, unattended support, and cloud-based management into a single, streamlined platform. With intuitive controls and enterprise-grade security, IT professionals can remotely diagnose issues, improve system performance, and reduce downtime from a centralized dashboard.
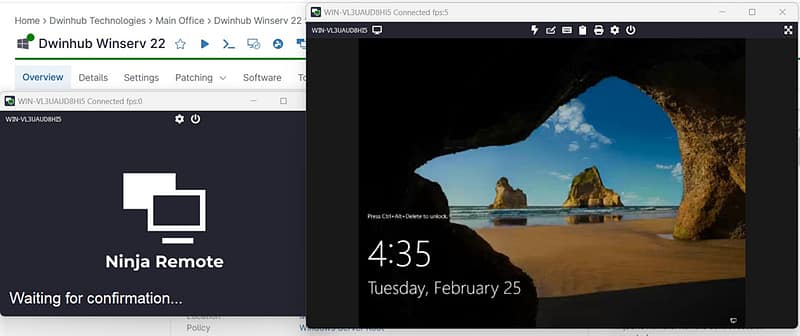
Empower IT Teams with Smarter Remote Support Solutions
Secure Remote Desktop Access
Unattended Troubleshooting Capabilities
Multi-Device Management Dashboard
Real-Time Collaboration Tools
Automated Performance Monitoring
Scalable Cloud-Based Infrastructure
Discover Powerful Remote IT Support Capabilities
Robust Remote Desktop Security
Proactive Unattended Access
Centralized Endpoint Dashboard
Rapid Session Initiation
Dynamic Bandwidth Optimization
Integrated Collaboration Tools
Optimize IT Support Across Every Scenario
Enterprise-Level Remote Workforce Support
Proactive Maintenance for Critical Infrastructure
MSP-Centric Secure Access Solutions
Upgrade your remote support strategy today!
Remote Troubleshooting Software FAQs
What is remote troubleshooting software?
Remote troubleshooting software enables IT teams to securely diagnose and resolve technical issues without needing on-site access. With secure remote desktop access, unattended support, and cloud-based management, technicians can monitor, control, and troubleshoot devices from a centralized dashboard. Designed for enterprise-grade security and efficiency, it streamlines IT workflows, reduces downtime, and improves system performance, ensuring faster issue resolution and a seamless support experience.
How does remote desktop troubleshooting work?
Remote desktop troubleshooting allows IT teams to diagnose and resolve issues on remote devices without on-site access. Using secure remote desktop access, technicians can view screens, run diagnostics, transfer files, and apply fixes in real time. With unattended remote access, they can troubleshoot devices even when users aren’t present. Integrated remote desktop management ensures secure session logging and monitoring, reducing downtime and improving IT efficiency.
Is remote troubleshooting safe?
Yes, remote desktop troubleshooting is safe when proper security measures are in place. Features like end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls ensure that only authorized users can initiate secure remote desktop access. Unattended remote access is tightly controlled, and remote desktop management tools log all sessions for compliance and auditing. With these safeguards, IT teams can troubleshoot devices remotely without compromising security.
How to troubleshoot a computer remotely?
To troubleshoot a computer remotely, start by establishing a secure connection and ensuring the device is online. Check system logs, firewall settings, and running processes to spot any issues. Use remote tools to update software, tweak settings, or restart services if needed. If it’s a hardware concern, check device managers and system health reports. When necessary, walk the user through manual fixes and document the solution to prevent future problems.
How to troubleshoot remote desktop connection?
To troubleshoot a remote desktop connection, first, ensure the remote device is powered on and reachable over the network. Check for connectivity issues by pinging the device or testing other network services. Verify that RDP or VNC is enabled, firewall rules allow the connection, and necessary ports (such as 3389 for RDP or 5900 for VNC) are open. If using a VPN, confirm it’s active and properly configured. Restart the remote desktop service, update network drivers, and check for software conflicts. If authentication fails, verify credentials and ensure the account has remote access permissions. Finally, test the connection from a different device or network to rule out local issues.
What's the difference between RDP and VNC?
The main difference between RDP versus VNC is how they handle remote access. RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) is designed for efficiency, transmitting graphical instructions instead of raw screen data, which makes it faster and more responsive. It allows full remote control, supports multiple sessions, and enables features like audio and printer redirection, but it typically logs out the local user during a session. RDP is ideal for on-demand remote access scenarios where IT teams need quick control over devices without user intervention.
VNC (Virtual Network Computing), on the other hand, shares the entire screen pixel by pixel, making it slower but more suitable for collaboration, as the local user remains logged in. VNC is cross-platform but lacks built-in encryption, requiring additional security measures. VNC is often used for ad-hoc troubleshooting situations where multiple users need to view and interact with the same session simultaneously.
In short, RDP is optimized for performance and full remote control, while VNC is better for shared access and platform compatibility.
Related Resources
Good to Great: Best Practices for Remote Management Success
Discover best practices to help you and your team access and monitor the endpoints that you manage.
4 Ways Technology Supports a Remote Workforce
Complete Guide: How to Manage IT Infrastructure Remotely


