NinjaOne Endpoint Security for Linux: Fortifying Your Digital Fortress
Enhance Linux security with confidence using NinjaOne Endpoint Security — ensuring strong protection, proactive threat detection, and efficient management for maximum security.
Streamlined IT Management
Improved Operational Efficiency
Reduced Risk and Enhanced Security
Unmatched Scalability and Flexibility
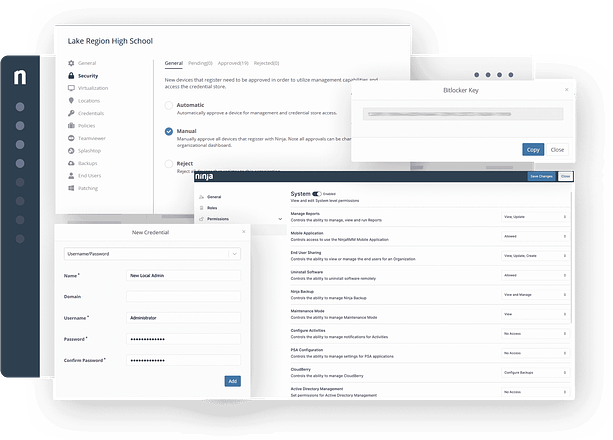
Key features of the Endpoint Security for Linux
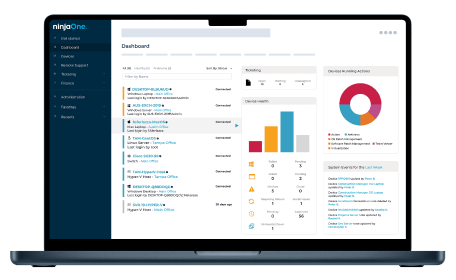
Real-time Monitoring and Reporting
Remote Device Management
Automation and Scripting
Scalability and Flexibility
NinjaOne scales seamlessly to cater to any organization size, easily accommodating growth and evolving infrastructure needs. NinjaOne’s endpoint agent can be deployed to cloud-based and on-premise machines, offering a tailored solution for diverse environments.
Vulnerability Management
Gain unparalleled visibility into your Linux fleet’s patch status, identifying and prioritizing critical vulnerabilities across diverse distributions (CentOS, Ubuntu, Fedora, etc.). Automated patching, coupled with granular approval workflows, ensures timely remediation, minimizing attack vectors.
Built for today’s IT teams
Streamlining Security Management for Diverse Linux Systems
Bolster Remote Access Security for Linux Systems
Enhance Vulnerability Management for Linux Fleets
Ready to fortify your Linux environment?
Endpoint Security for Linux FAQs
What is Endpoint Security for Linux?
Linux endpoint security entails employing a range of technologies and strategies to secure computer systems operating on the Linux OS against cyber threats like viruses, malware, and unauthorized access. The primary goal of endpoint security is to deploy a mix of tools, including firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems, to shield endpoint devices from attacks and thwart potential data breaches.
How does Linux endpoint security work?
Linux endpoint security employs a multi-layered approach to safeguard systems. This includes firewalls for network control, antivirus software to detect and remove malware, intrusion detection systems for monitoring, access controls to restrict unauthorized access, regular updates to address vulnerabilities, encryption for data protection, behavioral analysis to identify anomalies, and endpoint detection and response for real-time monitoring and incident response. Together, these measures create a robust defense against cyber threats on Linux-based systems.
What are Linux endpoints?
Linux endpoints refer to computing devices such as desktops, laptops, servers, and specialized hardware that operate on the Linux operating system. These endpoints play various roles within a networked environment, serving as user workstations, data servers, or specialized nodes. Linux endpoint security involves implementing measures like firewalls, antivirus software, access controls, and encryption to protect these devices from cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and functionality of Linux-based systems in diverse computing scenarios.


